Retrospective study on the therapeutic efficacy of zinc acetate hydrate administration to patients with hypozincemia-induced dysgeusia
- PMID: 36934261
- PMCID: PMC10024455
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-023-02866-7
Retrospective study on the therapeutic efficacy of zinc acetate hydrate administration to patients with hypozincemia-induced dysgeusia
Abstract
Background: Dysgeusia is a relatively early symptom of zinc deficiency, and zinc replacement is effective in treating dysgeusia. The administration of zinc acetate hydrate (ZAH) was approved in 2017 for patients with hypozincemia in Japan. This retrospective study was conducted to explore the efficacy and safety of ZAH administration in patients with hypozincemia-induced dysgeusia.
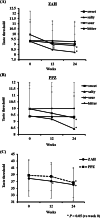
Methods: Patients with hypozincemia-induced dysgeusia who visited our hospital from May 2013 to December 2019 were included in this study. ZAH (zinc content; 50 mg/day) was administered to 42 patients for 24 weeks. The taste test was performed using the filter paper disk method, and the total cognitive thresholds of the left and right chorda tympani regions were used. Changes in taste function, serum zinc and copper levels, and copper/zinc ratio were analyzed. A total of 28 patients who received polaprezinc (PPZ, zinc content; 34 mg/day) for 24 weeks, who were prescribed until ZAH was approved, were registered as controls.
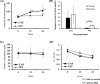
Results: Serum zinc levels at 12 and 24 weeks after ZAH or PPZ administration were higher than those before administration. These levels were significantly higher in the ZAH-treated group than in the PPZ-treated group. However, serum copper levels did not significantly change before and after administration. In the taste test, the taste thresholds for the acidity and salty at 12 and 24 weeks after ZAH administration were significantly decreased compared to before administration. In contrast, in the PPZ group, the taste thresholds for the acidity and salty were significantly decreased 24 weeks after administration.
Conclusions: ZAH (50 mg/day) administration was effective in improving the gustatory sensitivity of patients with dysgeusia and hypozincemia 12 weeks after administration without affecting the serum copper level. ZAH was also more effective than PPZ.
Keywords: Copper/zinc ratio; Dysgeusia; Hypocupremia; Hypozincemia; Zinc acetate hydrate.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of zinc acetate hydrate and polaprezinc for zinc deficiency in patients on maintenance hemodialysis: A single-center, open-label, prospective randomized study.Ther Apher Dial. 2020 Oct;24(5):568-577. doi: 10.1111/1744-9987.13461. Epub 2019 Dec 14. Ther Apher Dial. 2020. PMID: 31794152 Clinical Trial.
-
Zinc Acetate Hydrate Supplementation versus Polaprezinc Supplementation for Improving Hypozincemia in Hemodialysis Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Int J Nephrol. 2023 Oct 5;2023:2403755. doi: 10.1155/2023/2403755. eCollection 2023. Int J Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37840640 Free PMC article.
-
Multicenter, prospective, observational study of chemotherapy-induced dysgeusia in gastrointestinal cancer.Support Care Cancer. 2022 Jun;30(6):5351-5359. doi: 10.1007/s00520-022-06936-4. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Support Care Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35292848 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis and treatment of taste disorders in Japan.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2024 Feb;51(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2023.04.002. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2024. PMID: 37117102 Review.
-
The Significance of Zinc in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease.Nutrients. 2022 Nov 17;14(22):4855. doi: 10.3390/nu14224855. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36432541 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2, periodontal pathogens, and host factors: The trinity of oral post-acute sequelae of COVID-19.Rev Med Virol. 2024 May;34(3):e2543. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2543. Rev Med Virol. 2024. PMID: 38782605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zinc supplementation for dysgeusia in patients with unresectable pancreatic cancer.Int J Clin Oncol. 2024 Aug;29(8):1173-1181. doi: 10.1007/s10147-024-02544-w. Epub 2024 May 10. Int J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38724773
-
The zinc receptor, ZnR/GPR39, modulates taste sensitivity by regulating ion secretion in mouse salivary gland.iScience. 2025 Jan 28;28(2):111912. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.111912. eCollection 2025 Feb 21. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40017509 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Rehabilitation Therapy Is Effective for Physical Function in a Patient With Amyloid Light Chain Amyloidosis Complicated by Nephrotic Syndrome: A Case Report and Literature Review.Cureus. 2024 Jul 18;16(7):e64830. doi: 10.7759/cureus.64830. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39156469 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Henkin RI, et al. Idiopathic hypogeusia with dysgeusia, hyposmia, and dysosmia. A new syndrome JAMA. 1971;217(4):434–440. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

