Clinical outcomes of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 Omicron and Delta variant: systematic review and meta-analysis of 33 studies covering 6 037 144 coronavirus disease 2019-positive patients
- PMID: 36934872
- PMCID: PMC10023211
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmi.2023.03.017
Clinical outcomes of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 Omicron and Delta variant: systematic review and meta-analysis of 33 studies covering 6 037 144 coronavirus disease 2019-positive patients
Abstract
Background: Although the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant is considered to induce less severe disease, there have been no consistent results on the extent of the decrease in severity.
Objectives: To compare the clinical outcomes of COVID-19-positive patients with Omicron and Delta variant infection.
Data sources: Searches were implemented up to 8 November 2022 in PubMed, Web of Science, BioRvix, and MedRvix.
Study eligibility criteria: Eligible studies were cohort studies reporting the clinical outcomes of COVID-19-positive patients with Omicron and Delta variant infection, including hospitalization, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, receiving invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV), and death.
Participants: COVID-19-positive patients with Omicron and Delta variant infection.
Assessment of risk of bias: Risk of bias was assessed employing the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale.
Methods of data synthesis: Random-effect models were employed to pool the ORs and 95% CIs to compare the risk of clinical outcome. I2 was employed to evaluate the heterogeneity between studies.
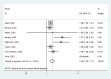
Results: A total of 33 studies with 6 037 144 COVID-19-positive patients were included in this meta-analysis. In the general population of COVID-19-positive patients, compared with Delta, Omicron variant infection resulted in a decreased risk of hospitalization (10.24% vs. 4.14%, OR = 2.91, 95% CI = 2.35-3.60), ICU admission (3.67% vs. 0.48%, OR = 3.64, 95% CI = 2.63-5.04), receiving IMV (3.93% vs. 0.34%, OR = 3.11, 95% CI = 1.76-5.50), and death (2.40% vs. 0.46%, OR = 2.97, 95% CI = 2.17-4.08). In the hospitalized patients with COVID-19, compared with Delta, Omicron variant infection resulted in a decreased risk of ICU admission (20.70% vs. 12.90%, OR = 1.63, 95% CI = 1.32-2.02), receiving IMV (10.90% vs. 5.80%, OR = 1.65, 95% CI = 1.28-2.14), and death (10.72% vs. 7.10%, OR = 1.44, 95% CI = 1.22-1.71).
Conclusions: Compared with Delta, the severity of Omicron variant infection decreased.
Keywords: Delta; Hospitalization; Meta-analysis; Omicron; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2023 European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures






References
-
- Graham M.S., Sudre C.H., May A., Antonelli M., Murray B., Varsavsky T., et al. Changes in symptomatology, reinfection, and transmissibility associated with the SARS-CoV-2 variant B.1.1.7: an ecological study. Lancet Public Health. 2021;6:e335–e345. doi: 10.1016/s2468-2667(21)00055-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kupferschmidt K., Wadman M. Delta variant triggers new phase in the pandemic. Science. 2021;372:1375–1376. doi: 10.1126/science.372.6549.1375. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

