A Bayesian network analysis of psychosocial risk and protective factors for suicidal ideation
- PMID: 36935710
- PMCID: PMC10014716
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1010264
A Bayesian network analysis of psychosocial risk and protective factors for suicidal ideation
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to investigate and model the interactions between a range of risk and protective factors for suicidal ideation using general population data collected during the critical phase of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods: Bayesian network analyses were applied to cross-sectional data collected 1 month after the COVID-19 lockdown measures were implemented in Austria and the United Kingdom. In nationally representative samples (n = 1,005 Austria; n = 1,006 UK), sociodemographic features and a multi-domain battery of health, wellbeing and quality of life (QOL) measures were completed. Predictive accuracy was examined using the area under the curve (AUC) within-sample (country) and out-of-sample.
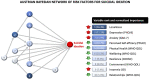
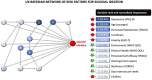
Results: The AUC of the Bayesian network models were ≥ 0.84 within-sample and ≥0.79 out-of-sample, explaining close to 50% of variability in suicidal ideation. In total, 15 interrelated risk and protective factors were identified. Seven of these factors were replicated in both countries: depressive symptoms, loneliness, anxiety symptoms, self-efficacy, resilience, QOL physical health, and QOL living environment.
Conclusions: Bayesian network models had high predictive accuracy. Several psychosocial risk and protective factors have complex interrelationships that influence suicidal ideation. It is possible to predict suicidal risk with high accuracy using this information.
Keywords: Bayesian network analysis; COVID-19; depression; risk factors; suicide.
Copyright © 2023 Delgadillo, Budimir, Barkham, Humer, Pieh and Probst.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Saxena S, Krug EG, Chestnov O. Preventing Suicide: A Global Imperative. World Health Organization (2014). Available online at: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241564779 (accessed July 27, 2020).
-
- Hasson-Ohayon I, Lysaker PH. Special challenges in psychotherapy continuation and adaption for persons with schizophrenia in the age of coronavirus (COVID-19). Couns Psychol Q. (2020) 17:1–9. 10.1080/09515070.2020.1781595 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

