Thirty-day and one-year outcomes following transcatheter mitral valve edge-to-edge repair versus transapical mitral valve replacement in patients with left ventricular dysfunction
- PMID: 36936096
- PMCID: PMC10020820
- DOI: 10.4244/AIJ-D-22-00049
Thirty-day and one-year outcomes following transcatheter mitral valve edge-to-edge repair versus transapical mitral valve replacement in patients with left ventricular dysfunction
Abstract
Background: A comparison of 30-day and 1-year clinical outcomes in patients with pre-existing left ventricular (LV) dysfunction undergoing transcatheter mitral valve edge-to-edge repair (TEER) or transcatheter transapical mitral valve replacement (TMVR) has not previously been reported.
Aims: We aimed to compare 30-day and 1-year rates of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality as well as rehospitalisation for heart failure (HFH).
Methods: All patients with severe (≥3+) symptomatic mitral regurgitation (MR) and an LV ejection fraction ≤50% who underwent TEER or TMVR over a 5-year period were evaluated.
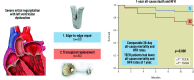
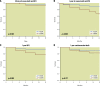
Results: Ninety-six patients (50 TEER, age 80±9 years, 70% secondary MR and 46 TMVR, age 72±9 years, 91% secondary MR) were studied. Baseline demographic and transthoracic echocardiogram characteristics were well-matched, with the exception of age (TEER 80±9 vs TMVR 72±9; p=0.01). Successful device implantation occurred in 96% of TEER patients and 97.8% of TMVR patients. Ninety-two percent of TEER patients had ≤2+MR predischarge, whilst no TMVR patient had ≥1+MR (p<0.01). No significant difference in the combined endpoint of 30-day all-cause mortality or HFH was observed (p>0.05). At 1 year, freedom from all-cause mortality and HFH was 79.2% across the entire study population but was significantly higher in patients undergoing TEER (TEER: n=45 [90%] hazard ratio 11.26, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 10.59-11.93 vs TMVR: n=39 [67.4%] 95% CI: 10.09-11.33; p=0.008).
Conclusions: Despite comparable rates of successful device implantation, MR reduction, and 30-day all-cause mortality/HFH, TEER patients had lower all-cause mortality and HFH rates at 1 year.
Conflict of interest statement
D.W.M. Muller is an advisory board member and consultant for Medtronic, Edwards Lifesciences, and Abbott Vascular; and has received research grant support from Abbott Vascular and Medtronic.A. Duncan and G. Dahle are consultants for Abbott Vascular. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Goliasch G, Bartko PE, Pavo N, Neuhold S, Wurm R, Mascherbauer J, Lang IM, Strunk G, Hülsmann M. Refining the prognostic impact of functional mitral regurgitation in chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:39–46. - PubMed
-
- Trichon BH, Felker GM, Shaw LK, Cabell CH, O'Connor CM. Relation of frequency and severity of mitral regurgitation to survival among patients with left ventricular systolic dysfunction and heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 2003;91:538–43. - PubMed
-
- Nishimura RA, Bonow RO. Percutaneous Repair of Secondary Mitral Regurgitation - A Tale of Two Trials. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:2374–6. - PubMed
-
- Obadia JF, Messika-Zeitoun D, Leurent G, Iung B, Bonnet G, Piriou N, Lefèvre T, Piot C, Rouleau F, Carrié D, Nejjari M, Ohlmann P, Leclercq F, Saint Etienne, Teiger E, Leroux L, Karam N, Michel N, Gilard M, Donal E, Trochu J-N, Cormier B, Armoiry X, Boutitie F, Maucort-Boulch D, Barnel C, Samson G, Guerin P, Vahanian A, Mewton N MITRA-FR Ivestigators. Percutaneous Repair or Medical Treatment for Secondary Mitral Regurgitation. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:2297–306. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

