Case report: A case of Culler-Jones syndrome caused by a novel mutation of GLI2 gene and literature review
- PMID: 36936162
- PMCID: PMC10020625
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1133492
Case report: A case of Culler-Jones syndrome caused by a novel mutation of GLI2 gene and literature review
Abstract
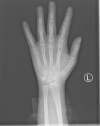
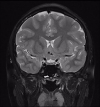
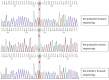
Culler-Jones syndrome is a rare clinical phenomenon with diverse manifestations and is prone to misdiagnosis. We report one patient who presented with a 10-year history of anosmia and a 1-year history of epididymal pain. Kallmann syndrome was suspected initially. The results of his laboratory tests, imaging, and genetic testing, however, combined to provide a conclusive diagnosis of Culler-Jones syndrome. With the aid of high-throughput sequencing technology, the GLI2 gene c.527A>G (p.Tyr176Cys) heterozygous mutation in the child was identified. No published works have yet described this mutation site. We described Culler-Jones syndrome in a child at length. We recommend that Culler-Jones syndrome be taken into account when considering the spectrum of disorders associated with abnormal growth and development in children. Once diagnosed, individualized hormone replacement treatment is required for each patient.
Keywords: Culler-Jones Syndrome; GLI2 gene; anosmia; high- throughput sequencing; hypogonadotropic hypogonadism.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Dong, Xue, Wang, Yan and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Clinical and genetic analysis of a child with Culler-Jones syndrome due to variant of GLI2 gene].Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2023 Feb 10;40(2):217-221. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn511389-20210927-00779. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 36709944 Chinese.
-
A novel truncating variant of GLI2 associated with Culler-Jones syndrome impairs Hedgehog signalling.PLoS One. 2019 Jan 10;14(1):e0210097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210097. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30629636 Free PMC article.
-
[Culler-Jones syndrome caused by a new mutated GLI2 gene: a case report].Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Dec 1;62(12):1472-1475. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20230322-00167. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 38044075 Chinese.
-
Kallmann Syndrome Due to Heterozygous Mutation in SOX10 Coexisting With Waardenburg Syndrome Type II: Case Report and Review of Literature.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Feb 1;11:592831. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.592831. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33597923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kallmann syndrome: phenotype and genotype of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism.Metabolism. 2018 Sep;86:124-134. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2017.10.012. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Metabolism. 2018. PMID: 29108899 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Demiral M, Demirbilek H. Ectopic posterior pituitary, polydactyly, midfacial hypoplasia and multiple pituitary hormone deficiency due to a novel heterozygous IVS11-2A>C(c.1957-2A>C) mutation in the GLI2 gene. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol (2020) 12(3):319–28. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2019.2019.0142 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Martín-Rivada Á, Rodríguez-Contreras FJ, Muñoz-Calvo MT, Güemes M, González-Casado I, Del Pozo JS, et al. . A novel GLI2 mutation responsible for congenital hypopituitarism and polymalformation syndrome. Growth hormone IGF Res Off J Growth Hormone Res Soc Int IGF Res Soc (2019) 44:17–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2018.12.002 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources