External validation and improvement of the scoring system for predicting the prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma after interventional therapy
- PMID: 36936655
- PMCID: PMC10020369
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2023.1045213
External validation and improvement of the scoring system for predicting the prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma after interventional therapy
Abstract
Background: Currently, locoregional therapies, such as transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and ablation, play an important role in the treatment of Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, an easy-to-use scoring system that predicts recurrence to guide individualized management of HCC with varying risks of recurrence remains an unmet need.
Methods: A total of 483 eligible HCC patients treated by TACE combined with ablation from January 1, 2017, to December 31, 2019, were included in the temporal external validation cohort and then used to explore possibilities for refinement of the original scoring system. We investigated the prognostic value of baseline variables on recurrence-free survival (RFS) using a Cox model and developed the easily applicable YA score. The performances of the original scoring system and YA score were assessed according to discrimination (area under the receiver operating curve [AUROC] and Harrell's concordance index [C-statistic]), calibration (calibration curves), and clinical utility [decision curve analysis (DCA) curves]. Finally, improvement in the ability to predict in the different scoring systems was assessed using the Net Reclassification Index (NRI). The YA score was lastly compared with other prognostic scores.
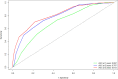
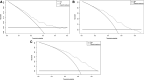
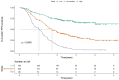
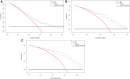
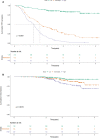
Results: During the median follow-up period of 35.6 months, 292 patients experienced recurrence. In the validation cohort, the original scoring system exhibited high discrimination (C-statistic: 0.695) and calibration for predicting the prognosis in HCC. To improve the prediction performance, the independent predictors of RFS, including gender, alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and des-γ-carboxyprothrombin (DCP), tumor number, tumor size, albumin-to-prealbumin ratio (APR), and fibrinogen, were incorporated into the YA score, an improved score. Compared to the original scoring system, the YA score has better discrimination (c-statistic: 0.712VS0.695), with outstanding calibration and the clinical net benefit, both in the training and validation cohorts. Moreover, the YA score accurately stratified patients with HCC into low-, intermediate- and high-risk groups of recurrence and mortality and outperformed other prognostic scores.
Conclusion: YA score is associated with recurrence and survival in early- and middle-stage HCC patients receiving local treatment. Such score would be valuable in guiding the monitoring of follow-up and the design of adjuvant treatment trials, providing highly informative data for clinical management decisions.
Keywords: HCC; TACE; ablation; external validation; recurrence; scoring system.
© 2023 Qiao, Wang, Mei, Wang, Wang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Jia Z, Zhang H, Li N. Evaluation of clinical outcomes of radiofrequency ablation and surgical resection for hepatocellular carcinoma conforming to the milan criteria: a systematic review and meta-analysis of recent randomized controlled trials. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2021) 36(7):1769–77. 10.1111/jgh.15440 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang C, Liao Y, Qiu J, Yuan Y, Zhang Y, Li K, et al. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization alone or combined with ablation for recurrent intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity score matching study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2020) 146(10):2669–80. 10.1007/s00432-020-03254-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

