Computed tomography-based COVID-19 triage through a deep neural network using mask-weighted global average pooling
- PMID: 36936770
- PMCID: PMC10020619
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1116285
Computed tomography-based COVID-19 triage through a deep neural network using mask-weighted global average pooling
Abstract
Background: There is an urgent need to find an effective and accurate method for triaging coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients from millions or billions of people. Therefore, this study aimed to develop a novel deep-learning approach for COVID-19 triage based on chest computed tomography (CT) images, including normal, pneumonia, and COVID-19 cases.
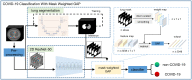
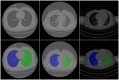
Methods: A total of 2,809 chest CT scans (1,105 COVID-19, 854 normal, and 850 non-3COVID-19 pneumonia cases) were acquired for this study and classified into the training set (n = 2,329) and test set (n = 480). A U-net-based convolutional neural network was used for lung segmentation, and a mask-weighted global average pooling (GAP) method was proposed for the deep neural network to improve the performance of COVID-19 classification between COVID-19 and normal or common pneumonia cases.
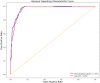
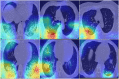
Results: The results for lung segmentation reached a dice value of 96.5% on 30 independent CT scans. The performance of the mask-weighted GAP method achieved the COVID-19 triage with a sensitivity of 96.5% and specificity of 87.8% using the testing dataset. The mask-weighted GAP method demonstrated 0.9% and 2% improvements in sensitivity and specificity, respectively, compared with the normal GAP. In addition, fusion images between the CT images and the highlighted area from the deep learning model using the Grad-CAM method, indicating the lesion region detected using the deep learning method, were drawn and could also be confirmed by radiologists.
Conclusions: This study proposed a mask-weighted GAP-based deep learning method and obtained promising results for COVID-19 triage based on chest CT images. Furthermore, it can be considered a convenient tool to assist doctors in diagnosing COVID-19.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; computed tomography (CT); coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19); deep learning; global average pooling (GAP).
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Sun, Zhou, Gao, Dong, Liu, Bai, Ma, Li, Li, Cai and Sheng.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Z-YS and GL were employed by Keya Medical Technology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
COVID-DSNet: A novel deep convolutional neural network for detection of coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) cases from CT and Chest X-Ray images.Artif Intell Med. 2022 Dec;134:102427. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2022.102427. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Artif Intell Med. 2022. PMID: 36462906 Free PMC article.
-
From community-acquired pneumonia to COVID-19: a deep learning-based method for quantitative analysis of COVID-19 on thick-section CT scans.Eur Radiol. 2020 Dec;30(12):6828-6837. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07042-x. Epub 2020 Jul 18. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32683550 Free PMC article.
-
Deep-learning algorithms for the interpretation of chest radiographs to aid in the triage of COVID-19 patients: A multicenter retrospective study.PLoS One. 2020 Nov 24;15(11):e0242759. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242759. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33232368 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of COVID-19 from CT and Chest X-ray Images Using Deep Learning Models.Ann Biomed Eng. 2022 Jul;50(7):825-835. doi: 10.1007/s10439-022-02958-5. Epub 2022 Apr 12. Ann Biomed Eng. 2022. PMID: 35415768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Overview of Deep Learning Techniques on Chest X-Ray and CT Scan Identification of COVID-19.Comput Math Methods Med. 2021 Jun 4;2021:5528144. doi: 10.1155/2021/5528144. eCollection 2021. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021. PMID: 34194535 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Joint Classification Method for COVID-19 Lesions Based on Deep Learning and Radiomics.Tomography. 2024 Sep 5;10(9):1488-1500. doi: 10.3390/tomography10090109. Tomography. 2024. PMID: 39330755 Free PMC article.
References
-
- An P., Xu S., Harmon S. A., Turkbey E. B., Sanford T. H., Amalou A., et al. . (2020). CT images in covid-19 [Data set]. Cancer Imaging Archive.
-
- Armato S. G., McLennan G., Bidaut L., McNitt-Gray M. F., Meyer C. R., Reeves A. P., et al. . (2011). The lung image database consortium (LIDC) and image database resource initiative (IDRI): A completed reference database of lung nodules on CT scans. Med. Phys. 38 (2), 915–931. doi: 10.1118/1.3528204 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

