Neuronal loss of NCLX-dependent mitochondrial calcium efflux mediates age-associated cognitive decline
- PMID: 36936788
- PMCID: PMC10014305
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106296
Neuronal loss of NCLX-dependent mitochondrial calcium efflux mediates age-associated cognitive decline
Abstract
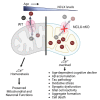
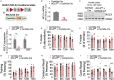
Mitochondrial calcium overload contributes to neurodegenerative disease development and progression. We recently reported that loss of the mitochondrial sodium/calcium exchanger (NCLX), the primary mechanism of mCa2+ efflux, promotes mCa2+ overload, metabolic derangement, redox stress, and cognitive decline in models of Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, whether disrupted mCa2+ signaling contributes to neuronal pathology and cognitive decline independent of pre-existing amyloid or tau pathology remains unknown. Here, we generated mice with neuronal deletion of the mitochondrial sodium/calcium exchanger (NCLX, Slc8b1 gene), and evaluated age-associated changes in cognitive function and neuropathology. Neuronal loss of NCLX resulted in an age-dependent decline in spatial and cued recall memory, moderate amyloid deposition, mild tau pathology, synaptic remodeling, and indications of cell death. These results demonstrate that loss of NCLX-dependent mCa2+ efflux alone is sufficient to induce an Alzheimer's disease-like pathology and highlights the promise of therapies targeting mCa2+ exchange.
Keywords: Behavioral neuroscience; Cellular neuroscience; Cognitive neuroscience; Molecular neuroscience.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests related to this work. J.W.E. is a paid consultant for Mitobridge, Inc., An Astellas Company.
Figures




References
-
- Jack C.R., Jr., Bennett D.A., Blennow K., Carrillo M.C., Dunn B., Haeberlein S.B., Holtzman D.M., Jagust W., Jessen F., Karlawish J., et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: toward a biological definition of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2018;14:535–562. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.02.018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- P01 HL147841/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL142271/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AG065445/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL136954/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 NS121379/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F30 AG082407/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL134608/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS121379/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL123966/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL091804/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072947/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DK120876/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

