Surgical Excision for Refractory Ischiogluteal Bursitis: A Consecutive Case Series of 21 Patients
- PMID: 36937219
- PMCID: PMC10020732
- DOI: 10.5371/hp.2023.35.1.24
Surgical Excision for Refractory Ischiogluteal Bursitis: A Consecutive Case Series of 21 Patients
Abstract
Purpose: A response to conservative treatment is usually obtained in cases of ischiogluteal bursitis. However, the time required to achieve relief of symptoms can vary from days to weeks, and there is a high recurrence rate, thus invasive treatment in addition to conservative treatment can occasionally be effective. Therefore, the aim of this study was to examine surgical excision in cases of refractory ischiogluteal bursitis and to evaluate patients' progression and outcome.
Materials and methods: A review of 21 patients who underwent surgical excision for treatment of ischiogluteal bursitis between February 2009 and July 2020 was conducted. Of these patients, seven patients were male, and 14 patients were female. Injection of steroid and local anesthetic into the ischial bursa was administered at outpatient clinics in all patients, who and they were refractory to conservative treatment, including aspiration and prescription drugs. Therefore, surgery was considered necessary. Excisions were performed by two orthopedic specialists using a direct vertical incision on the ischial area. A review of each patient was performed after excision, and quantification of the outcomes recorded using clinical scoring systems was performed.
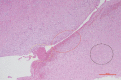
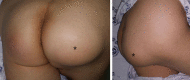
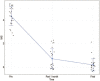
Results: The results of radiologic evaluation showed that the mean lesion size was 6.2 cm×4.5 cm×3.6 cm. The average disease course after excision was 21.6 days (range, 15-48 days). Measurement of clinical scores, including the visual analog scale and Harris hip scores, was performed during periodic visits, with scores of 0.7 (range, 0-2) and 98.1 (range, 96-100) at one postoperative month, respectively.
Conclusion: Surgical excision, with an expectation of favorable results, could be considered for treatment of ischiogluteal bursitis that is refractory to therapeutic injections, aspirations, and medical prescriptions, particularly in moderate-to-severe cases.
Keywords: Ischiogluteal bursitis; Surgical excision.
Copyright © 2023 by Korean Hip Society.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest relevant to this article.
Figures


References
-
- Johnson DB, Varacallo M. Piriformis syndrome. Ischial bursitis: StatPearls Publishing; 2001. StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482285/ - PubMed
-
- Hitora T, Kawaguchi Y, Mori M, et al. Ischiogluteal bursitis: a report of three cases with MR findings. Rheumatol Int. 2009;29:455–458. - PubMed
-
- Akisue T, Yamamoto T, Marui T, et al. Ischiogluteal bursitis: multimodality imaging findings. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;(406):214–217. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

