SeDeM expert system with I-optimal mixture design for oral multiparticulate drug delivery: An encapsulated floating minitablets of loxoprofen Na and its in silico physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling
- PMID: 36937845
- PMCID: PMC10022826
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1066018
SeDeM expert system with I-optimal mixture design for oral multiparticulate drug delivery: An encapsulated floating minitablets of loxoprofen Na and its in silico physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling
Abstract
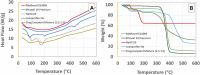
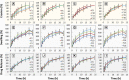
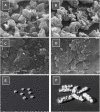
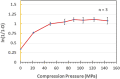
Introduction: A SeDeM expert tool-driven I-optimal mixture design has been used to develop a directly compressible multiparticulate based extended release minitablets for gastro-retentive drug delivery systems using loxoprofen sodium as a model drug. Methods: Powder blends were subjected to stress drug-excipient compatibility studies using FTIR, thermogravimetric analysis, and DSC. SeDeM diagram expert tool was utilized to assess the suitability of the drug and excipients for direct compression. The formulations were designed using an I-optimal mixture design with proportions of methocel K100M, ethocel 10P and NaHCO3 as variables. Powder was compressed into minitablets and encapsulated. After physicochemical evaluation lag-time, floating time, and drug release were studied. Heckel analysis for yield pressure and accelerated stability studies were performed as per ICH guidelines. The in silico PBPK Advanced Compartmental and Transit model of GastroPlus™ was used for predicting in vivo pharmacokinetic parameters. Results: Drug release follows first-order kinetics with fickian diffusion as the main mechanism for most of the formulations; however, a few formulations followed anomalous transport as the mechanism of drug release. The in-silico-based pharmacokinetic revealed relative bioavailability of 97.0%. Discussion: SeDeM expert system effectively used in QbD based development of encapsulated multiparticulates for once daily administration of loxoprofen sodium having predictable in-vivo bioavailability.
Keywords: SeDeM expert tool; extended release minitablets; in silico PBPK; loxoprofen Na; multiparticulate drug delivery system.
Copyright © 2023 Rauf-ur-Rehman, Shoaib, Ahmed, Yousuf, Siddiqui, Saleem, Qazi, Khan, Irshad, Bashir, Naz, Farooq and Mahmood.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Aguilar-Díaz J. E., García-Montoya E., Pérez-Lozano P., Suñe-Negre J. M., Miñarro M., Ticó J. R. (2009). The use of the SeDeM diagram expert system to determine the suitability of diluents–disintegrants for direct compression and their use in formulation of ODT,. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 73, 414–423. 10.1016/j.ejpb.2009.07.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ahmed F. R., Shoaib M. H., Yousuf R. I., Ali T., Geckeler K. E., Siddiqui F., et al. (2019). Clay nanotubes as a novel multifunctional excipient for the development of directly compressible diclofenac potassium tablets in a SeDeM driven QbD environment. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 133, 214–227. 10.1016/j.ejps.2019.03.028 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ajay B., Dinesh K., Pradeep S. (2010). Studies on formulation and evaluation of floating tablets of ciprofloxacin. Int. J. Compren Pharma 5, 1–3.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

