Comparative pharmacokinetics of four major compounds after oral administration of Mori Cortex total flavonoid extract in normal and diabetic rats
- PMID: 36937873
- PMCID: PMC10014546
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1148332
Comparative pharmacokinetics of four major compounds after oral administration of Mori Cortex total flavonoid extract in normal and diabetic rats
Abstract
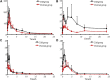
Introduction: Mori Cortex has been used in traditional Chinese Medicine as an antidiabetic agent. The aim of this study was to establish a UPLC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of morin, morusin, umbelliferone and mulberroside A in rat plasma and investigate the pharmacokinetics differences between normal and diabetic rats following oral administration of Mori Cortex total flavonoid extract. Methods: Samples were pre-treated by protein precipitation and genkwanin was used as internal standard. Chromatographic separation was performed using a Hypersil GOLD C18 column (50 mm × 2.1 mm, 3 μm). The mobile phase consisted of acetonitrile and water (containing 0.1% formic acid) in gradient mode at a flow rate of 0.5 ml/min. The transitions of m/z 300.9→107.1, m/z 419.3→297.1, m/z 160.9→77.0, m/z 567.1→243.2 and m/z 283.1→268.2 were selected for morin, morusin, umbelliferone, mulberroside A and internal standard, respectively. Results: The intra- and inter-day precision for analytes were less than 12.5% and the accuracy ranged from -8.1% to 3.5%. The extraction recovery was >88.5% and no obvious matrix effect was observed. The AUC (0-t) and C max of morin were 501.3 ± 115.5 ng/mL*h and 127.8 ± 56.0 ng/mL in normal rats and 717.3 ± 117.4 ng/ml*h and 218.6 ± 33.5 ng/ml in diabetic rats. Meanwhile, the AUC (0-t) and C max of morusin were 116.4 ± 38.2 ng/ml*h and 16.8 ± 10.1 ng/mL in normal rats and 325.0 ± 87.6 ng/mL*h and 39.2 ± 5.9 ng/ml in diabetic rats. For umbelliferone and mulberroside A, the AUC (0-t) and C max also increased significantly in diabetic rats (p < 0.05). Discussion: The validated method was successfully applied to the pharmacokinetic study in normal and diabetic rats.
Keywords: Mori Cortex total flavonoid extract; UPLC-MS/MS; diabetes mellitus; pharmacokinetic; rats.
Copyright © 2023 Xiong, Li, Chu, Deng, Sun, Liu, Mu and Yao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bayazid A. B., Kim J. G., Park S. H., Lim B. O. (2020). Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiproliferative activity of Mori cortex radicis extracts. Nat. Prod. Commun. 15 (1), 1934578X1989976–8. 10.1177/1934578x19899765 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

