The relation between radiographic manifestation and clinical characteristics of congenital radioulnar synostosis in children: A retrospective study from multiple centers
- PMID: 36937958
- PMCID: PMC10020496
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2023.1117060
The relation between radiographic manifestation and clinical characteristics of congenital radioulnar synostosis in children: A retrospective study from multiple centers
Abstract
Objective: To review the radiographic manifestation and clinical appearance of children with congenital radioulnar synostosis (CRUS) retrospectively.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study of children with CRUS from multiple medical centers.
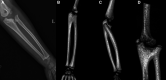
Results: A total of 329 patients (male 259, female 70) with an average age of 5.4 years (0.5-16 years old), were included in this study. In particular, 145 patients (145/329, 44.1%) demonstrated bilateral involvement, and 184 patients (left 123, right 61) demonstrated unilateral involvement. As for Clear and Omery (C&O) classification, most patients belonged to Type III, and then followed by Type IV. As for Chinese Multi-center Pediatric Orthopedic Study Group (CMPOS) classification, most patients belonged to Type III, and then followed by Type II and Type I. In C&O Type III, 92.03% patients demonstrated severe pronation. According to CMPOS classification, 92.98% Type I patients demonstrated neutral to mild pronation, 72.17% Type II patients demonstrated moderate pronation, and 92.03% Type III patients demonstrated severe pronation. The age distribution showed no significant difference between C&O Type II and IV (P = 0.96); the pronation ankylosis severity showed no significant difference between C&O Type II and IV (P = 0.387).
Conclusion: Although CRUS is a rare forearm deformity, there are certain relation between radiographic manifestation and clinical forearm functional restriction. CRUS patients of C&O or CMPOS Type III classification might suffer severe pronation deformity and warrant early intervention.
Keywords: ankylosis; classification; congenital radioulnar synostosis; pronation; radiographic manifestation.
© 2023 Hong, Tan, Zhou, Zheng, Li, Zheng and Tang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials