Randomized Phase 2 Trial of Telitacicept in Patients With IgA Nephropathy With Persistent Proteinuria
- PMID: 36938094
- PMCID: PMC10014376
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2022.12.014
Randomized Phase 2 Trial of Telitacicept in Patients With IgA Nephropathy With Persistent Proteinuria
Abstract
Introduction: To date, no specific therapies have been approved for immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) treatment. Telitacicept is a fusion protein composed of transmembrane activator and calcium-modulating cyclophilin ligand interactor and fragment crystallizable portion of immunoglobulin G (IgG), which neutralizes the B lymphocyte stimulator and a proliferation-inducing ligand.
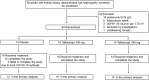
Methods: This phase 2 randomized placebo-controlled trial aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of telitacicept in patients with IgAN. Participants with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) >35 ml/min per 1.73 m2 and proteinuria ≥0.75 g/d despite optimal supportive therapy, were randomized 1:1:1 to receive subcutaneous telitacicept 160 mg, telitacicept 240 mg, or placebo weekly for 24 weeks. The primary end point was the change in 24-hour proteinuria at week 24 from baseline.
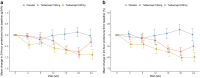
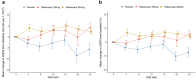
Results: Forty-four participants were randomized into placebo (n = 14), telitacicept 160 mg (n = 16), and telitacicept 240 mg (n = 14) groups. Continuous reductions in serum IgA, IgG, and IgM levels were observed in the telitacicept group. Telitacicept 240 mg therapy reduced mean proteinuria by 49% from baseline (change in proteinuria vs. placebo, 0.88; 95% confidence interval, -1.57 to -0.20; P = 0.013), whereas telitacicept 160 mg reduced it by 25% (-0.29; 95% confidence interval, -0.95 to 0.37; P = 0.389). The eGFR remained stable over time. Adverse events (AEs) were similar in all groups. Treatment-emergent AEs were mild or moderate, and no severe AEs were reported.
Conclusion: Telitacicept treatment led to a clinically meaningful reduction in proteinuria in patients with IgAN in the present phase 2 clinical trial. This effect is indicative of a reduced risk for future kidney disease progression.
Keywords: BLyS/APRIL inhibitors; IgA Nephropathy; TACI-Fc fusion protein; proteinuria; telitacicept.
© 2022 Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of the International Society of Nephrology.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

