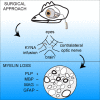
Development of a new surgical technique to infuse kynurenic acid to optic nerves in chickens for studying loss of myelination
- PMID: 36938412
- PMCID: PMC10020079
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14361
Development of a new surgical technique to infuse kynurenic acid to optic nerves in chickens for studying loss of myelination
Abstract
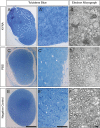
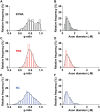
Prolonged infusion of a high dose of kynurenic acid (KYNA) reduces the myelin content in the rat spinal cord with preservation of the axonal integrity and without inducing an inflammatory response. We hypothesized that subdural infusion of a high concentration of KYNA can induce myelin loss in the optic nerves (ONs) of chickens. However, existing methods to deliver agents to the ON are inefficient, unlocalized and provide only acute exposure. Thus, we developed a surgical approach for sustained delivery of KYNA to the chicken ON. In brief, the novel surgical technique, which does not include excision of the extraocular muscles, involves incision of the skin and underlying fascial sheath to access the optic nerve within the muscle cone, implantation of a catheter in the dura of the optic nerve, the other end of which exits the orbit under the skin. The catheter runs under the skin near the lateral canthus, over the ears to the back of the neck, where a second incision is made to both implant the osmotic pump and to attach the catheter to the osmotic pump. India ink was used to confirm prolonged sustained administration to the optic nerves and across the chiasm. This surgical model was used to investigate KYNA's effect(s) on myelin loss in the ON. ONs of 7-day old chickens were infused with 50 mM KYNA or phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for seven days. Analysis of KYNA-infused contralateral ON g-ratios and protein levels indicated a reduction in myelin. These findings demonstrate the utility of our surgical approach for sustained delivery of KYNA into the ON and suggest a role for KYNA in modulating CNS myelination.
Keywords: CNS, central nervous system; Chicken; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; Infusion; KYNA, kynurenic acid; Kynurenic acid; MAG, myelin associated glycoprotein; MBP, myelin basic protein; Myelin; NC, negative control; ON, optic nerve; Optic nerve; PBS, phosphate buffered saline; PLP, proteolipid protein; Subdural.
© 2023 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prolonged Subdural Infusion of Kynurenic Acid Is Associated with Dose-Dependent Myelin Damage in the Rat Spinal Cord.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 12;10(11):e0142598. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142598. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26562835 Free PMC article.
-
Axons modulate myelin protein messenger RNA levels during central nervous system myelination in vivo.J Neurosci Res. 1990 Aug;26(4):409-18. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490260403. J Neurosci Res. 1990. PMID: 1700137
-
Rumpshaker: an X-linked mutation causing hypomyelination: developmental differences in myelination and glial cells between the optic nerve and spinal cord.Glia. 1992;5(3):161-70. doi: 10.1002/glia.440050302. Glia. 1992. PMID: 1375190
-
A Review of the Health Benefits of Food Enriched with Kynurenic Acid.Nutrients. 2022 Oct 8;14(19):4182. doi: 10.3390/nu14194182. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36235834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myelination and axonal regeneration in the central nervous system of mice deficient in the myelin-associated glycoprotein.J Neurocytol. 1996 May;25(5):303-13. doi: 10.1007/BF02284804. J Neurocytol. 1996. PMID: 8818975 Review.
Cited by
-
Intestinal tryptophan metabolism in disease prevention and swine production.Anim Nutr. 2023 Aug 19;15:364-374. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2023.08.002. eCollection 2023 Dec. Anim Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38058568 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Moroni F. Tryptophan metabolism and brain function: focus on kynurenine and other indole metabolites. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999;375:87–100. - PubMed
-
- Perkins M.N., Stone T.W. An iontophoretic investigation of the actions of convulsant kynurenines and their interaction with the endogenous excitant quinolinic acid. Brain Res. 1982;247:184–187. - PubMed
-
- Hilmas C., Pereira E.F.R., Alkondon M., Rassoulpour A., Schwarcz R., Albuquerque E.X. The brain metabolite kynurenic acid inhibits alpha-7 nicotinic receptor activity and increases non-alpha-7 nicotinic receptor expression: physiopathological implications. J. Neurosci. 2001;21:7463–7473. - PMC - PubMed
-
- DiNatale B.C., Murray I.A., Schroeder J.C., Flaveny C.A., Lahoti T.S., Laurenzana E.M., Omiecinski C.J., Perdew G.H. Kynurenic acid is a potent endogenous aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand that synergistically induces interleukin-6 in the presence of inflammatory signaling. Toxicol. Sci. 2010;115:89–97. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq024. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

