Does deep learning software improve the consistency and performance of radiologists with various levels of experience in assessing bi-parametric prostate MRI?
- PMID: 36939953
- PMCID: PMC10027972
- DOI: 10.1186/s13244-023-01386-w
Does deep learning software improve the consistency and performance of radiologists with various levels of experience in assessing bi-parametric prostate MRI?
Abstract
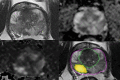
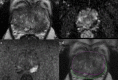
Objective: To investigate whether commercially available deep learning (DL) software improves the Prostate Imaging-Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) scoring consistency on bi-parametric MRI among radiologists with various levels of experience; to assess whether the DL software improves the performance of the radiologists in identifying clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa).
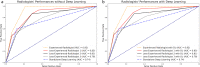
Methods: We retrospectively enrolled consecutive men who underwent bi-parametric prostate MRI at a 3 T scanner due to suspicion of PCa. Four radiologists with 2, 3, 5, and > 20 years of experience evaluated the bi-parametric prostate MRI scans with and without the DL software. Whole-mount pathology or MRI/ultrasound fusion-guided biopsy was the reference. The area under the receiver operating curve (AUROC) was calculated for each radiologist with and without the DL software and compared using De Long's test. In addition, the inter-rater agreement was investigated using kappa statistics.
Results: In all, 153 men with a mean age of 63.59 ± 7.56 years (range 53-80) were enrolled in the study. In the study sample, 45 men (29.80%) had clinically significant PCa. During the reading with the DL software, the radiologists changed their initial scores in 1/153 (0.65%), 2/153 (1.3%), 0/153 (0%), and 3/153 (1.9%) of the patients, yielding no significant increase in the AUROC (p > 0.05). Fleiss' kappa scores among the radiologists were 0.39 and 0.40 with and without the DL software (p = 0.56).
Conclusions: The commercially available DL software does not increase the consistency of the bi-parametric PI-RADS scoring or csPCa detection performance of radiologists with varying levels of experience.
Keywords: Deep learning; Magnetic resonance imaging; Prostate cancer.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
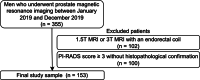


Similar articles
-
Anatomically guided self-adapting deep neural network for clinically significant prostate cancer detection on bi-parametric MRI: a multi-center study.Insights Imaging. 2023 Jun 19;14(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s13244-023-01439-0. Insights Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37337101 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic magnetic resonance imaging for primary prostate cancer evaluation: Diagnostic potential of a non-contrast-enhanced bi-parametric approach enhanced with relaxometry measurements.Eur J Radiol Open. 2022 Feb 15;9:100403. doi: 10.1016/j.ejro.2022.100403. eCollection 2022. Eur J Radiol Open. 2022. PMID: 35242886 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted MRI/TRUS fusion-guided biopsy in men with previous prostate biopsies using a novel registration software and multiparametric MRI PI-RADS scores: first results.World J Urol. 2015 Nov;33(11):1707-14. doi: 10.1007/s00345-015-1525-4. Epub 2015 Mar 14. World J Urol. 2015. PMID: 25774003
-
[The diagnostic value of version 2.1 prostate imaging reporting and data system for prostate transitional zone lesions].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Dec 8;100(45):3609-3613. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20200506-01442. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33333685 Chinese.
-
Comparative Performance of Deep Learning and Radiologists for the Diagnosis and Localization of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer at MRI: A Systematic Review.Life (Basel). 2022 Sep 26;12(10):1490. doi: 10.3390/life12101490. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36294928 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent trends in AI applications for pelvic MRI: a comprehensive review.Radiol Med. 2024 Sep;129(9):1275-1287. doi: 10.1007/s11547-024-01861-4. Epub 2024 Aug 3. Radiol Med. 2024. PMID: 39096356 Review.
References
-
- Westphalen AC, McCulloch CE, Anaokar JM, et al. Variability of the positive predictive value of PI-RADS for prostate MRI across 26 centers: experience of the society of abdominal radiology prostate cancer disease-focused panel. Radiology. 2020;296:76–84. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020190646. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

