Effectiveness of photodynamic therapy (PDT) in the management of symptomatic oral lichen planus -A systematic review
- PMID: 36941903
- PMCID: PMC10023948
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2023.03.003
Effectiveness of photodynamic therapy (PDT) in the management of symptomatic oral lichen planus -A systematic review
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding missing Declaration of competing interest statements in previously published articles.J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2024 Jul-Aug;14(4):353-354. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2024.05.011. Epub 2024 May 22. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2024. PMID: 38826838 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Oral Lichen Planus (OLP) is a chronic mucocutaneous inflammatory disease of unknown aetiology characterized by T cell mediated autoimmune response which trigger apoptosis of basal cells of an oral epithelium. Corticosteroids are the primary therapeutic option for symptomatic OLP however treatment of lesions unresponsive to corticosteroids that tend to recur are becoming challenging for the clinicians. Currently photodynamic therapy (PDT) is being explored as a new curative option for reduction of pain and/or burning sensation associated with OLP lesions.
Aims and objective: The aim of this systematic review was to analyse studies from literature on the therapeutic effectiveness of PDT in management of symptomatic OLP unresponsive to corticosteroid therapy.
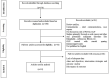
Methods: The electronic retrieval systems and databases PUBMED [MEDLINE], EMBASE, SCOPUS, WEB OF SCIENCE, GOOGLE SCHOLAR, and SCIENCE DIRECT were searched independently by two authors for relevant articles from January 2015 till July 2021. Primary studies focussed on the role of PDT in treatment of symptomatic OLP and published in English were included.
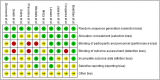
Results: Out of the 370 articles, only ten studies met the selection criteria. Included studies demonstrated PDT as an effective alternative modality to treat symptomatic OLP with no drop outs. In all studies, with PDT reduction in lesion size and VAS score was observed during each follow up sessions and after treatment (approx. 12 weeks) when compared to pre-treatment level (p < 0.001). Four studies noted PDT to be more effective than topical corticosteroids in reduction of signs and symptoms of OLP (p = 0.001).
Conclusion: In the future, long-term studies on larger population should be conducted to establish the clinical effectiveness in PDT in symptomatic OLP. Studies should take into consideration different sources of light and photosensitizers to determine the ideal parameters of PDT treatment for OLP. Wavelength is the most important factor in all types of photo therapies, so the most appropriate wavelength should be selected to obtain better outcome.
Keywords: Corticosteroids; Oral lichen planus; Photodynamic therapy; Treatment.
© 2023 The Authors.
Figures


References
-
- Silverman S., Jr. Oral lichen planus: a potentially premalignant lesion. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000;58(11):1286–1288. - PubMed
-
- González-Moles, Warnakulasurya S., Gonzalez-Ruiz I., et al. Worldwide prevalence of oral lichen planus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Dis. 2021 May;27(4):813–828. - PubMed
-
- Roopashree M.R., Gondhalekar R.V., Shashikanth M.C., George J., Thippeswamy S.H., Shukla A. Pathogenesis of oral lichen planus--a review. J Oral Pathol Med. 2010 Nov;39(10):729–734. - PubMed
-
- Scully C., Eisen D., Carrozzo M. Management of oral lichen planus. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2000;1(5):287–306. - PubMed
-
- Abdel-kader Mahmoud H. 2016. CHAPTER 1:The Journey of PDT throughout History: PDT from Pharos to Present , inPhotodynamic Medicine: From Bench to Clinic; pp. 1–21.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

