Electrochemical detection and quantification of catechol based on a simple and sensitive poly(riboflavin) modified carbon nanotube paste electrode
- PMID: 36942251
- PMCID: PMC10023950
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14378
Electrochemical detection and quantification of catechol based on a simple and sensitive poly(riboflavin) modified carbon nanotube paste electrode
Abstract
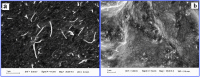
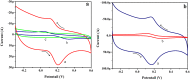
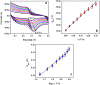
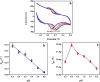
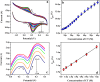
In the present research work, selective and sensitive catechol (CT) detection and quantification were shown in the presence of resorcinol (RS) in 0.2 M phosphate buffer (PB) solution by preparing a low-cost, simple, and green carbon nanotube paste electrode (CNTPE) surface activated with electropolymerized riboflavin (PRF). The morphological, conductivity, and electrochemical features of the modified electrode (PRFMCNTPE) and bare carbon nanotube paste electrode (BCNTPE) materials were analyzed using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), cyclic voltammetry (CV), and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV). The PRF-activated electrode displays outstanding sensitivity, stability, selectivity, reproducibility, and repeatability for the redox feature of CT with improved electrochemical current and declined electrochemical potential compared to BCNTPE. The peak currents of CT are correlated to the different CT concentrations (CV method: 6.0-60.0 μM & DPV method: 0.5-7.0 μM), and the obtained detection limit (DL) and quantification limit (QL) are found to be 0.025 μM and 0.085 μM (CV method) and 0.0039 μM and 0.0132 μM (DPV method), respectively. The prepared PRFMCNTPE material was advantageous for the examination of CT in environmentally important tap water sample as a real-time application.
Keywords: Carbon nanotube paste electrode; Catechol; Electrochemical sensor; Poly(Riboflavin); Resorcinol; Voltammetry; Water sample analysis.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Josep S., Saiz‐Poseu J., Busqué F., Ruiz‐Molina D. Catechol‐based biomimetic functional materials. Adv. Mater. 2013;25:653–701. - PubMed
-
- Patil N., Jerome C., Detrembleur C. Recent advances in the synthesis of catechol-derived (bio) polymers for applications in energy storage and environment. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018;82:34–91.
-
- Hirosawa I., Asaeda G., Arizono H., Shimbo S.I., Ikeda M. Effects of catechol on human subjects. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health. 1976;37:107–114. - PubMed
-
- Wang J., Yang J., Xu P., Liu H., Zhang L., Zhang S., Tian L. Gold nanoparticles decorated biochar modified electrode for the high-performance simultaneous determination of hydroquinone and catechol. Sens. Actuators, B. 2020;306
-
- Yu X., Wang N., Wang C., Gao W., Chen M., Liu N., Duan J., Hou B. Electrochemical detection of hydroquinone and catechol with covalent organic framework modified carbon paste electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020;877
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

