Transcriptional Self-Regulation of the Master Nitrogen Regulator GlnR in Mycobacteria
- PMID: 36943048
- PMCID: PMC10127674
- DOI: 10.1128/jb.00479-22
Transcriptional Self-Regulation of the Master Nitrogen Regulator GlnR in Mycobacteria
Abstract
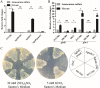
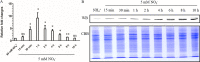
As a master nitrogen regulator in most actinomycetes, GlnR both governs central nitrogen metabolism and regulates many carbon, phosphate, and secondary metabolic pathways. To date, most studies have been focused on the GlnR regulon, while little is known about the transcriptional regulator for glnR itself. It has been observed that glnR transcription can be upregulated in Mycobacterium smegmatis under nitrogen-limited growth conditions; however, the detailed regulatory mechanism is still unclear. Here, we demonstrate that the glnR gene in M. smegmatis is transcriptionally activated by its product GlnR in response to nitrogen limitation. The precise GlnR binding site was successfully characterized in its promoter region using the electrophoretic mobility shift assay and the DNase I footprinting assay. Site mutagenesis and genetic analyses confirmed that the binding site was essential for in vivo self-activation of glnR transcription. Moreover, based on bioinformatic analyses, we discovered that most of the mycobacterial glnR promoter regions (144 out of 147) contain potential GlnR binding sites, and we subsequently proved that the purified M. smegmatis GlnR protein could specifically bind 16 promoter regions that represent 119 mycobacterial species, including Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Together, our findings not only elucidate the transcriptional self-regulation mechanism of glnR transcription in M. smegmatis but also indicate the ubiquity of the mechanism in other mycobacterial species. IMPORTANCE In actinomycetes, the nitrogen metabolism not only is essential for the construction of life macromolecules but also affects the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites and even virulence (e.g., Mycobacterium tuberculosis). The transcriptional regulation of genes involved in nitrogen metabolism has been thoroughly studied and involves the master nitrogen regulator GlnR. However, the transcriptional regulation of glnR itself remains elusive. Here, we demonstrated that GlnR functions as a transcriptional self-activator in response to nitrogen starvation in the fast-growing model Mycobacterium species Mycobacterium smegmatis. We further showed that this self-regulation mechanism could be widespread in other mycobacteria, which might be beneficial for those slow-growing mycobacteria to adapt to the nitrogen-starvation environments such as within human macrophages for M. tuberculosis.
Keywords: GlnR; mycobacteria; nitrogen metabolism; self-activation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Research progress on GlnR-mediated regulation in Actinomycetes.Front Microbiol. 2023 Nov 22;14:1282523. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1282523. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38075861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The global nitrogen regulator GlnR is a direct transcriptional repressor of the key gluconeogenic gene pckA in actinomycetes.J Bacteriol. 2024 May 23;206(5):e0000324. doi: 10.1128/jb.00003-24. Epub 2024 Apr 12. J Bacteriol. 2024. PMID: 38606980 Free PMC article.
-
The Nitrogen Regulator GlnR Directly Controls Transcription of the prpDBC Operon Involved in Methylcitrate Cycle in Mycobacterium smegmatis.J Bacteriol. 2019 Mar 26;201(8):e00099-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00099-19. Print 2019 Apr 15. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 30745367 Free PMC article.
-
GlnR-mediated regulation of KstR controls cholesterol catabolism in Mycobacterium smegmatis.Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2022 Jun;69(3):1209-1216. doi: 10.1002/bab.2197. Epub 2021 May 27. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2022. PMID: 34008246
-
The Balance Metabolism Safety Net: Integration of Stress Signals by Interacting Transcriptional Factors in Streptomyces and Related Actinobacteria.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jan 22;10:3120. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.03120. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32038560 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Orphan response regulator NnaR is critical for nitrate and nitrite assimilation in Mycobacterium abscessus.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 May 24;14:1411333. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1411333. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38854658 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on GlnR-mediated regulation in Actinomycetes.Front Microbiol. 2023 Nov 22;14:1282523. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1282523. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38075861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The global nitrogen regulator GlnR is a direct transcriptional repressor of the key gluconeogenic gene pckA in actinomycetes.J Bacteriol. 2024 May 23;206(5):e0000324. doi: 10.1128/jb.00003-24. Epub 2024 Apr 12. J Bacteriol. 2024. PMID: 38606980 Free PMC article.
-
Design of a sorbitol-activated nitrogen metabolism-dependent regulatory system for redirection of carbon metabolism flow in Bacillus licheniformis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Nov 27;51(21):11952-11966. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad859. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37850640 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial metabolism disrupts cytokine activity to impact host immune response.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Nov 12;121(46):e2405719121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2405719121. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39514319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tiffert Y, Supra P, Wurm R, Wohlleben W, Wagner R, Reuther J. 2008. The Streptomyces coelicolor GlnR regulon: identification of new GlnR targets and evidence for a central role of GlnR in nitrogen metabolism in actinomycetes. Mol Microbiol 67:861–880. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.06092.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

