IL-6 in the infarcted heart is preferentially formed by fibroblasts and modulated by purinergic signaling
- PMID: 36943408
- PMCID: PMC10232006
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI163799
IL-6 in the infarcted heart is preferentially formed by fibroblasts and modulated by purinergic signaling
Abstract
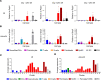
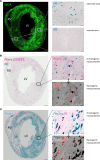
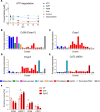
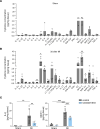
Plasma IL-6 is elevated after myocardial infarction (MI) and is associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Which cardiac cell type preferentially contributes to IL-6 expression and how its production is regulated are largely unknown. Here, we studied the cellular source and purinergic regulation of IL-6 formation in a murine MI model. We found that IL-6, measured in various cell types in post-MI hearts at the protein level and by quantitative PCR and RNAscope, was preferentially formed by cardiac fibroblasts (CFs). Single-cell RNA-Seq (scRNA-Seq) in infarcted mouse and human hearts confirmed this finding. We found that adenosine stimulated fibroblast IL-6 formation via the adenosine receptor A2bR in a Gq-dependent manner. CFs highly expressed Adora2b and rapidly degraded extracellular ATP to AMP but lacked CD73. In mice and humans, scRNA-Seq revealed that Adora2B was also mainly expressed by fibroblasts. We assessed global IL-6 production in isolated hearts from mice lacking CD73 on T cells (CD4-CD73-/-), a condition known to be associated with adverse cardiac remodeling. The ischemia-induced release of IL-6 was strongly attenuated in CD4-CD73-/- mice, suggesting adenosine-mediated modulation. Together, these findings demonstrate that post-MI IL-6 was mainly derived from activated CFs and was controlled by T cell-derived adenosine. We show that purinergic metabolic cooperation between CFs and T cells is a mechanism that modulates IL-6 formation by the heart and has therapeutic potential.
Keywords: Cardiology; Cytokines; Inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Comment in
- Interleukin 6 helps weave the inflammatory web during acute coronary syndromes doi: 10.1172/JCI167670
References
-
- Ridker PM, et al. Modulation of the interleukin-6 signalling pathway and incidence rates of atherosclerotic events and all-cause mortality: analyses from the Canakinumab Anti-Inflammatory Thrombosis Outcomes Study (CANTOS) Eur Heart J. 2018;39(38):3499–3507. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy310. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

