Once-Weekly Basal Insulin Fc Demonstrated Similar Glycemic Control to Once-Daily Insulin Degludec in Insulin-Naive Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Phase 2 Randomized Control Trial
- PMID: 36944059
- PMCID: PMC10154646
- DOI: 10.2337/dc22-2396
Once-Weekly Basal Insulin Fc Demonstrated Similar Glycemic Control to Once-Daily Insulin Degludec in Insulin-Naive Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Phase 2 Randomized Control Trial
Abstract
Objective: Basal insulin Fc (BIF) (insulin efsitora alfa; LY3209590), a fusion protein combining a novel single-chain insulin variant with a human IgG Fc domain, is designed for once-weekly basal insulin administration. This phase 2 study assessed the safety and efficacy of BIF versus degludec in insulin-naive patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) previously treated with oral antihyperglycemic medications.
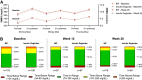
Research design and methods: During this randomized, parallel, open-label study, 278 insulin-naive patients with T2D were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive BIF once weekly or degludec once daily over the 26-week treatment period. Both groups were titrated to fasting glucose of 80-100 mg/dL (4.4 to <5.6 mmol/L). The primary end point was HbA1c change from baseline to week 26 (noninferiority margin 0.4%). Secondary end points included fasting blood glucose (FBG), six-point glucose profiles, and rate of hypoglycemia.
Results: After 26 weeks of treatment, BIF demonstrated a noninferior HbA1c change from baseline versus degludec, with a treatment difference of 0.06% (90% CI -0.11, 0.24; P = 0.56). Both BIF and degludec treatment led to significant reductions in FBG from baseline. At week 26, the between-treatment difference for BIF versus degludec was 4.7 mg/dL (90% CI 0.1, 9.3; P = 0.09). The rate of level 2 hypoglycemia was low and not significantly different between treatment groups (BIF 0.22 events/patient/year, degludec 0.15 events/patient/year; P = 0.64); there was no severe hypoglycemia. The occurrence of treatment-emergent adverse events was also similar between BIF and degludec.
Conclusions: Once-weekly BIF achieved excellent glycemic control similar to degludec, with no concerning hypoglycemia or other safety findings.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04450394.
© 2023 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
In type 2 diabetes, weekly basal insulin Fc was noninferior to daily insulin degludec for HbA1c at 26 wk.Ann Intern Med. 2023 Jul;176(7):JC81. doi: 10.7326/J23-0046. Epub 2023 Jul 4. Ann Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 37399561
References
-
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee . 6. Glycemic targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022;45(Suppl. 1):S83–S96 - PubMed
-
- Buse JB, Nauck M, Forst T, et al. . Exenatide once weekly versus liraglutide once daily in patients with type 2 diabetes (DURATION-6): a randomised, open-label study. Lancet 2013;381:117–124 - PubMed

