Paracetamol and ibuprofen combination for the management of acute mild-to-moderate pain in children: expert consensus using the Nominal Group Technique (NGT)
- PMID: 36945023
- PMCID: PMC10031994
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-023-01445-4
Paracetamol and ibuprofen combination for the management of acute mild-to-moderate pain in children: expert consensus using the Nominal Group Technique (NGT)
Abstract
Background: Acute pain is a common symptom in children of all ages, and is associated with a variety of conditions. Despite the availability of guidelines, pain often remains underestimated and undertreated. Paracetamol and ibuprofen are the most commonly used drugs for analgesia in Pediatrics. Multimodal pain management by using a combination of paracetamol and ibuprofen results in greater analgesia.
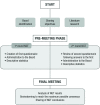
Methods: An investigation using the Nominal Group Technique was carried out between May and August 2022. Two open (non-anonymous) questionnaires were consecutively sent to a Board of ten clinicians to understand their opinions on the use of the oral paracetamol and ibuprofen association. Answers were examined in a final meeting where conclusions were drawn.
Results: The board achieved a final consensus on a better analgesic power of paracetamol and ibuprofen in fixed-dose combination as compared to monotherapy, without compromising safety. Strong consensus was reached on the opinion that the fixed-dose combination of paracetamol and ibuprofen may be a useful option in case of inefficacy of one or other drug as monotherapy, especially in case of headaches, odontalgia, earache, and musculoskeletal pain. The use of the fixed combination may be also considered suitable for postoperative pain management.
Conclusions: The use of the fixed-dose combination may represent advantage in terms of efficacy and safety, allowing a better control of the dose of both paracetamol and ibuprofen as monotherapy, thus minimizing the risk of incorrect dosage. However, the limited evidence available highlights the need for future well designed studies to better define the advantages of this formulation in the various therapeutic areas.
Keywords: Acute pain; Children; Fixed-dose; Ibuprofen; Paracetamol; Pediatric.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
-
- International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP). (2021) Pain in Children: Management. Available at: https://www.iasp-pain.org/resources/fact-sheets/pain-in-children-managem....
-
- Benini F, Corsini I, Castagno E, Silvagni D, Lucarelli A, Giacomelli L, Amigoni A, Ancora G, Astuto M, Borrometi F, Casilli RM, Chiappini E, Cutrera R, De Matteis A, di Mauro G, Musolino A, Fabbri A, Ferrero F, Fornaro M, Gangemi M, Lago P, Macrì F, Manfredini L, Memo L, Minicucci A, Petralia P, Pinelli N, Antonucci R, Tajè S, Tizi E, Venturelli L, Zampogna S, Urbino AF. COnsensus on Pediatric Pain in the Emergency Room: the COPPER project, issued by 17 Italian scientific societies. Ital J Pediatr. 2020;46(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s13052-020-00858-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed