This is a preprint.
MicroMagnify: a multiplexed expansion microscopy method for pathogens and infected tissues
- PMID: 36945526
- PMCID: PMC10029075
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2637060/v1
MicroMagnify: a multiplexed expansion microscopy method for pathogens and infected tissues
Update in
-
MicroMagnify: A Multiplexed Expansion Microscopy Method for Pathogens and Infected Tissues.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Oct;10(30):e2302249. doi: 10.1002/advs.202302249. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37658522 Free PMC article.
Abstract
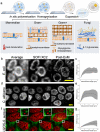
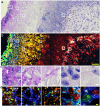
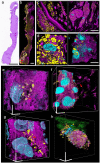
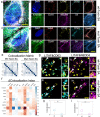
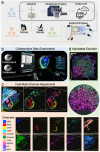
Super-resolution optical imaging tools are crucial in microbiology to understand the complex structures and behavior of microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses. However, the capabilities of these tools, particularly when it comes to imaging pathogens and infected tissues, remain limited. We developed µMagnify, a nanoscale multiplexed imaging method for pathogens and infected tissues that are derived from an expansion microscopy technique with a universal biomolecular anchor. We formulated an enzyme cocktail specifically designed for robust cell wall digestion and expansion of microbial cells without distortion while efficiently retaining biomolecules suitable for high-plex fluorescence imaging with nanoscale precision. Additionally, we developed an associated virtual reality tool to facilitate the visualization and navigation of complex three-dimensional images generated by this method in an immersive environment allowing collaborative exploration among researchers around the world. µMagnify is a valuable imaging platform for studying how microbes interact with their host systems and enables development of new diagnosis strategies against infectious diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): YZ, ZC, BRG, APM and AK are inventors on several inventions related to ExM. TS is the founder of Immersive Science LLC. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

