This is a preprint.
The cell type composition of the adult mouse brain revealed by single cell and spatial genomics
- PMID: 36945580
- PMCID: PMC10028805
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.03.06.531307
The cell type composition of the adult mouse brain revealed by single cell and spatial genomics
Abstract
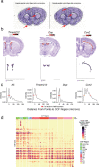
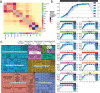
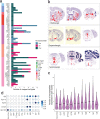
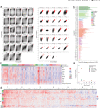
The function of the mammalian brain relies upon the specification and spatial positioning of diversely specialized cell types. Yet, the molecular identities of the cell types, and their positions within individual anatomical structures, remain incompletely known. To construct a comprehensive atlas of cell types in each brain structure, we paired high-throughput single-nucleus RNA-seq with Slide-seq-a recently developed spatial transcriptomics method with near-cellular resolution-across the entire mouse brain. Integration of these datasets revealed the cell type composition of each neuroanatomical structure. Cell type diversity was found to be remarkably high in the midbrain, hindbrain, and hypothalamus, with most clusters requiring a combination of at least three discrete gene expression markers to uniquely define them. Using these data, we developed a framework for genetically accessing each cell type, comprehensively characterized neuropeptide and neurotransmitter signaling, elucidated region-specific specializations in activity-regulated gene expression, and ascertained the heritability enrichment of neurological and psychiatric phenotypes. These data, available as an online resource (BrainCellData.org) should find diverse applications across neuroscience, including the construction of new genetic tools, and the prioritization of specific cell types and circuits in the study of brain diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests E.Z.M. and F.C. are academic founders of Curio Bioscience.
Figures


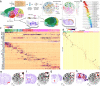
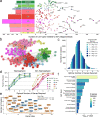



References
-
- Zeng H. & Sanes J. R. Neuronal cell-type classification: challenges, opportunities and the path forward. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 18, 530–546 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
