The current status of cancer survivorship care and a consideration of appropriate care model in Korea
- PMID: 36945714
- PMCID: PMC9942731
- DOI: 10.14216/kjco.20017
The current status of cancer survivorship care and a consideration of appropriate care model in Korea
Abstract
Purpose: Breast cancer patients with a human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) enriched subtype are known to have higher rates of brain metastases (BM) than other patients. This study aimed to evaluate treatment options and survival outcomes.
Methods: A total of 115 breast cancer brain metastases (BCBM) patients with nearly complete medical records were retrospectively analyzed. Additionally, 36 patients were HER2 enriched types according to histological subtypes. The BM was found by brain magnetic resonance imaging in patients who had neurologic symptoms or by regular screening. Age, breast tumor size, number of BM, histological subtypes, first treatment of breast cancer, estrogen receptor, and HER2 status, stage, local treatment of BM were analyzed. Median overall survival, 5-year survival were analyzed from the data.
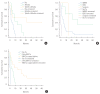
Results: The median survival time after BM was 6 months, the mean survival time was 16.3 months, and the 5-year survival after BM was only 8.0%. Factors that significantly affect the survival of BCBM patients include histological subtype, number of BM, use of lapatinib in multivariate analysis. A total of 19 out of 36 HER2 enriched patients were treated with lapatinib or capecitabine. For the treatment of HER2 enriched patients, additional use of blood-brain barrier (BBB) crossing substances, as well as local treatment for BM, significantly improve the survival rate in the Kaplan-Meier method (P=0.001).
Conclusion: A combination of local treatment modality for BCBM and the use of substances that cross the BBB for the HER2 enriched patient improved the survival rate.
Keywords: Blood-brain barrier; Brain neoplasms; Breast neoplasms.
Copyright © 2020 Korean Society of Surgical Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Tham YL, Sexton K, Kramer R, Hilsenbeck S, Elledge R. Primary breast cancer phenotypes associated with propensity for central nervous system metastases. Cancer. 2006;107:696–704. - PubMed
-
- Pestalozzi BC, Zahrieh D, Price KN, Holmberg SB, Lindtner J, Collins J, et al. Identifying breast cancer patients at risk for central nervous system (CNS) metastases in trials of the International Breast Cancer Study Group (IBCSG) Ann Oncol. 2006;17:935–44. - PubMed
-
- Gabos Z, Sinha R, Hanson J, Chauhan N, Hugh J, Mackey JR, et al. Prognostic significance of human epidermal growth factor receptor positivity for the development of brain metastasis after newly diagnosed breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:5658–63. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous