Monitoring renal oxygenation status by near-infrared spectroscopy during ureterorenoscopy in children
- PMID: 36945986
- PMCID: PMC10390123
- DOI: 10.55730/1300-0144.5544
Monitoring renal oxygenation status by near-infrared spectroscopy during ureterorenoscopy in children
Abstract
Background: : Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) monitoring demonstrates renal blood flow, perfusion, and oxygenation changes. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of pediatric endourological interventions (PEI) on regional oxygen saturation value (rSO2) usingrenal NIRS monitoring.
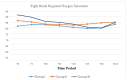
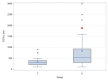
Methods: Patients having bilateral inguinal surgery (group I), cystoscopy (group II), and ureterorenoscopy (group III), 20 patients in each group, were included in the study. NIRS values before induction (T0) and at 5 min (T5), 10 min (T10), 15 min (T15), 20 min (T20), 25 min (T25), 30 min (T30) of the surgical procedure, and at the postextubation (Tend) were determined. The amount of irrigation fluid was recorded in groups II and III. The ureterorenoscopy group was also evaluated as two subgroups, as group III-R with patients having a "20%↓rSO2" and as group III-NoR, not having a "20%↓rSO2".
Results: The mean total volume of irrigation was higher in group III, but the difference was not significant between the subgroups III-R and III-NoR. Renal rSO2 decreased significantly in T25, T30, and T-end values in group III. "20%↓rSO2" was seen in 1 patient in group II and 7 patients in group III. In the subgroups III-R, all patients had an obstructive pathology and significant preoperative hydronephrosis with a mean renal pelvis AP diameter of 21.1 ± 16.4 mm.
Discussion: Although rSO2 significantly improves postoperatively, our data may suggest that congenital and acquired obstructive pathologies with hydronephrosis, prolonged operative time with continuous irrigation, and instrument movement in a narrow lumen may increase intrarenal pressure and the risk of renal hypoxia in endourological interventions. Preoperative evaluation of kidney functions and a meticulously well-planned intervention can prevent possible complications.
Keywords: Near-infrared spectroscopy; children; endourology; renal oxygenation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tokas T, Herrmann TRW, Skolarikos A, Nagele U. Training and Research in Urological Surgery and Technology (T.R.U.S.T.)-Group. Pressure matters: intrarenal pressures during normal and pathological conditions, and impact of increased values to renal physiology. World Journal of Urology. 2019;37(1):125–131. doi: 10.1007/s00345-018-2378-4. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials