Six-month effective treatment of corneal graft rejection
- PMID: 36947612
- PMCID: PMC10032610
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adf4608
Six-month effective treatment of corneal graft rejection
Abstract
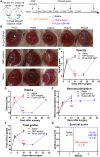
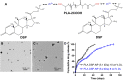
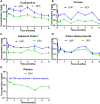
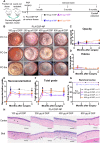
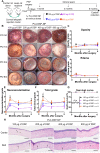
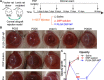
Topical corticosteroid eye drop is the mainstay for preventing and treating corneal graft rejection. While the frequent topical corticosteroid use is associated with risk of intraocular pressure (IOP) elevation and poor patient compliance that leads to graft failure and the requirement for a repeated, high-risk corneal transplantation. Here, we developed dexamethasone sodium phosphate (DSP)-loaded dicarboxyl-terminated poly(lactic acid) nanoparticle (PLA DSP-NP) formulations with relatively high drug loading (8 to 10 weight %) and 6 months of sustained intraocular DSP delivery in rats with a single dosing. PLA DSP-NP successfully reversed early signs of corneal rejection, leading to rat corneal graft survival for at least 6 months. Efficacious PLA DSP-NP doses did not affect IOP and showed no signs of ocular toxicity in rats for up to 6 months. Subconjunctival injection of DSP-NP is a promising approach for safely preventing and treating corneal graft rejection with the potential for improved patient adherence.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization, Blindness and vision impairment (2020);www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/blindness-and-visual-impairment.
-
- D. T. H. Tan, J. K. G. Dart, E. J. Holland, S. Kinoshita, Corneal transplantation. Lancet 379, 1749–1761 (2012). - PubMed
-
- P. Gain, R. Jullienne, Z. He, M. Aldossary, S. Acquart, F. Cognasse, G. Thuret, Global Survey of Corneal Transplantation and Eye Banking. JAMA Ophthalmol. 134, 167–173 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

