Brady- and tachyarrhythmias detected by continuous rhythm monitoring in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 36948572
- PMCID: PMC10423524
- DOI: 10.1136/heartjnl-2022-322253
Brady- and tachyarrhythmias detected by continuous rhythm monitoring in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
Abstract
Objective: Atrial fibrillation (AF) is associated with adverse events including conduction disturbances, ventricular arrhythmias and sudden death. The aim of this study was to examine brady- and tachyarrhythmias using continuous rhythm monitoring in patients with paroxysmal self-terminating AF (PAF).
Methods: In this multicentre observational substudy to the Reappraisal of Atrial Fibrillation: interaction between hyperCoagulability, Electrical remodelling and Vascular destabilisation in the progression of AF (RACE V), we included 392 patients with PAF and at least 2 years of continuous rhythm monitoring. All patients received an implantable loop recorder, and all detected episodes of tachycardia ≥182 beats per minute (BPM), bradycardia ≤30 BPM or pauses ≥5 s were adjudicated by three physicians.
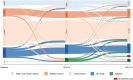
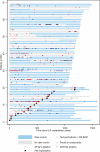
Results: Over 1272 patient-years of continuous rhythm monitoring, we adjudicated 1940 episodes in 175 patients (45%): 106 (27%) patients experienced rapid AF or atrial flutter (AFL), pauses ≥5 s or bradycardias ≤30 BPM occurred in 47 (12%) patients and in 22 (6%) patients, we observed both episode types. No sustained ventricular tachycardias occurred. In the multivariable analysis, age >70 years (HR 2.3, 95% CI 1.4 to 3.9), longer PR interval (HR 1.9, 1.1-3.1), CHA2DS2-VASc score ≥2 (HR 2.2, 1.1-4.5) and treatment with verapamil or diltiazem (HR 0.4, 0.2-1.0) were significantly associated with bradyarrhythmia episodes. Age >70 years was associated with lower rates of tachyarrhythmias.
Conclusions: In a cohort exclusive to patients with PAF, almost half experienced severe bradyarrhythmias or AF/AFL with rapid ventricular rates. Our data highlight a higher than anticipated bradyarrhythmia risk in PAF.
Trial registration number: NCT02726698.
Keywords: arrhythmias, cardiac; atrial fibrillation; bradycardia; electrophysiology; tachycardia, supraventricular.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: MHJPF received speakers’ honorarium from Medtronic outside submitted work. RGT reports grants from Medtronic and Abbott, and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer and Pfizer/Bristol Myers Squibb all outside submitted work. RGT is coinventor of the MyDiagnostick, not receiving royalties for the past 5 years. MDM is a Medtronic employee and WP Coordinator in the H2020 ITN My-Atria (No: 766082). IVG and AHM serve on the editorial board of BMJ Heart. The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
Bradyarrhythmias in patients with atrial fibrillation.Heart. 2023 Aug 11;109(17):1266-1268. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2023-322498. Heart. 2023. PMID: 37012041 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
