Asciminib monotherapy in patients with CML-CP without BCR::ABL1 T315I mutations treated with at least two prior TKIs: 4-year phase 1 safety and efficacy results
- PMID: 36949155
- PMCID: PMC10169635
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-023-01860-w
Asciminib monotherapy in patients with CML-CP without BCR::ABL1 T315I mutations treated with at least two prior TKIs: 4-year phase 1 safety and efficacy results
Abstract
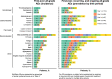
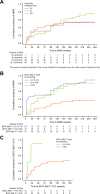
Asciminib is approved for patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia (CML-CP) who received ≥2 prior tyrosine kinase inhibitors or have the T315I mutation. We report updated results of a phase 1, open-label, nonrandomized trial (NCT02081378) assessing the safety, tolerability, and antileukemic activity of asciminib monotherapy 10-200 mg once or twice daily in 115 patients with CML-CP without T315I (data cutoff: January 6, 2021). After ≈4-year median exposure, 69.6% of patients remained on asciminib. The most common grade ≥3 adverse events (AEs) included increased pancreatic enzymes (22.6%), thrombocytopenia (13.9%), hypertension (13.0%), and neutropenia (12.2%); all-grade AEs (mostly grade 1/2) included musculoskeletal pain (59.1%), upper respiratory tract infection (41.7%), and fatigue (40.9%). Clinical pancreatitis and arterial occlusive events (AOEs) occurred in 7.0% and 8.7%, respectively. Most AEs occurred during year 1; the subsequent likelihood of new events, including AOEs, was low. By data cutoff, among patients without the indicated response at baseline, 61.3% achieved BCR::ABL1 ≤ 1%, 61.6% achieved ≤0.1% (major molecular response [MMR]), and 33.7% achieved ≤0.01% on the International Scale. MMR was maintained in 48/53 patients who achieved it and 19/20 who were in MMR at screening, supporting the long-term safety and efficacy of asciminib in this population.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
MJM: Bristol Myers Squibb, Takeda, and Pfizer: personal fees. TPH: Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Enliven: consultancy, research funding. D-WK: Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, IL-YANG, and Takeda: grants. DR: Novartis, Pfizer, and Incyte: personal fees. JEC: Novartis, Pfizer, and Bristol Myers Squibb: grants, consulting fees. AH: Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer: institutional research support; Novartis and Incyte: institutional research support, personal fees. KS: Novartis: research funding, honoraria. MB: Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Pfizer, Incyte, and Novartis: consultancy and honoraria; AbbVie: consultancy. MT: IMAGO: consultancy; Novartis and Takeda: research funding; Constellation Pharmaceuticals and Bristol Myers Squibb: membership on board of directors or advisory committees. OO: Amgen, Incyte, Celgene, Roche, Fusion Pharma, Novartis: honoraria. Amgen, Incyte, and Celgene: research funding. HM: Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb Japan, Celgene, Chugai Pharma, Daiichi Sankyo, Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma, Eisai, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Lilly Japan, Novartis, Ono Pharmaceutical, Otsuka, Pfizer, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Takeda, MSD, and AbbVie: honoraria; Ono Pharmaceutical: consulting; Astellas Pharma, Chugai Pharma, Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma, Eisai, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Lilly Japan, Ono Pharmaceutical, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Nippon Shinyaku, MSD, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi Sankyo, Takeda, Nihonkayaku, Shionogi, Sanofi, Bayer Schering Pharma, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, and Teijin Pharma: research funding. YTG: Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, Amgen, MSD Pharma, Novartis, EUSA Pharma, Roche, Bristol Myers Squibb, and AbbVie: honoraria. DJD: AbbVie, Novartis, Blueprint, and GlycoMimetics: grants; AbbVie, Novartis, Blueprint and GlycoMimetics: research funding; AbbVie, Amgen, Autolus, Blueprint, Forty-Seven, GlycoMimetics, Incyte, Jazz, Kite, Novartis, Pfizer, Servier, and Takeda; consulting. AbbvVie, Amgen, Autolus, Blueprint, Forty-Seven, GlycoMimetics, Incyte, Jazz, Kite, Novartis, Pfizer, Servier, and Takeda: personal fees. MCH: Novartis, Deciphera, Theseus and Blueprint Medicines: consultancy; Deciphera: speaker’s bureau; Jonathan David Foundation, VA Merit Review Grant (I01BX005358), and NCI R21 grant (R21CA263400): partial salary support. Prior to 2019, MCH held an equity interest in MolecularMD. MCH holds multiple patents on the diagnosis and/or treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors; one patent on treatment has been licensed by Oregon Health & Science University to Novartis. VGGdS: Novartis, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Incyte: grants, nonfinancial support, and honoraria. PC: Pfizer, Novartis, and Incyte: honoraria. F-XM: Novartis: grants, honoraria, consultancy, and research funding; Bristol Myers Squibb and Pfizer: honoraria. JJWMJ: Novartis and Bristol Myers Squibb: research funding; Incyte: speaker’s fee; AbbVie, Novartis, Pfizer, and Incyte: honoraria; AbbVie, Alexion, Amgen, Astellas, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Janssen-Cilag, Olympus, Incyte, Sanofi Genzyme, Servier, Jazz, and Takeda: support for Apps for Care and Science nonprofit foundation of which JJWMJ is president. MD: Fusion Pharma, Blueprint, Pfizer, Novartis, Medscape, and Sangoma: consultancy; Pfizer: research funding; Takeda, Sangomo, and Blueprint: membership on board of directors or advisory committees. NS: Novartis: honoraria. Amgen: support for attending meetings and/or travel. MBG: National Cancer Institute, Amgen, Sanofi, Actinium Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: grants; Allogene: consulting. Sanofi and American Society of Hematology: honoraria. SC, FP, NA, and MH are employees of Novartis. FL: Bristol Myers Squibb, Incyte, and Celgene: consultancy, honoraria; Novartis: consultancy, honoraria, and research funding.
Figures


References
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. 2022;V1.2023.
-
- Hirji I, Gupta S, Goren A, Chirovsky DR, Moadel AB, Olavarria E, et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML): association of treatment satisfaction, negative medication experience and treatment restrictions with health outcomes, from the patient’s perspective. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2013;11:167. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-11-167. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

