Characterization and investigation of electrochemical and biological properties of antibacterial silver nanoparticle-deposited TiO2 nanotube array surfaces
- PMID: 36949171
- PMCID: PMC10033515
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-31937-6
Characterization and investigation of electrochemical and biological properties of antibacterial silver nanoparticle-deposited TiO2 nanotube array surfaces
Abstract
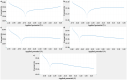
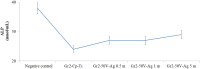
The one of main reasons of the premature failure of Ti-based implants is infections. The metal- and metal oxide-based nanoparticles have very high potential on controlling of infections. In this work, the randomly distributed AgNPs-deposited onto well-ordered TiO2 nanotube surfaces were fabricated on titanium by anodic oxidation (AO) and electrochemical deposition (ED) processes. AgNPs-deposited nanotube surfaces, which is beneficial for bone tissue growth exhibited hydrophilic behaviors. Moreover, the AgNPs-deposited nanotube surfaces, which prevent the leaching of metallic Ti ions from the implant surface, indicated great corrosion resistance under SBF conditions. The electrochemical corrosion resistance of AgNPs-deposited nanotube surfaces was improved up to about 145% compared to bare Gr2 surface. The cell viability of AgNPs-deposited nanotube surfaces was improved. Importantly, the AgNPs-deposited nanotube surfaces exhibited antibacterial activity for Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Eventually, it can be concluded that the AgNPs-deposited nanotube surfaces possess high stability for long-term usage of implant applications.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Hou X, Aitola K, Lund PD. TiO2 nanotubes for dye-sensitized solar cells—A review. Energy Sci. Eng. 2021;9:921–937. doi: 10.1002/ese3.831. - DOI
-
- Arifin K, Yunus RM, Minggu LJ, Kassim MB. Improvement of TiO2 nanotubes for photoelectrochemical water splitting: Review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 2021;46:4998–5024. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.11.063. - DOI
-
- Bindra P, Hazra A. Selective detection of organic vapors using TiO2 nanotubes based single sensor at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019;290:684–690. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2019.03.115. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

