A prospective analysis of the long-term impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on well-being and health care among children with a chronic condition and their families: a study protocol of the KICK-COVID study
- PMID: 36949465
- PMCID: PMC10031163
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-023-03912-7
A prospective analysis of the long-term impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on well-being and health care among children with a chronic condition and their families: a study protocol of the KICK-COVID study
Abstract
Background: There is consistent evidence that the COVID-19 pandemic is associated with an increased psychosocial burden on children and adolescents and their parents. Relatively little is known about its particular impact on high-risk groups with chronic physical health conditions (CCs). Therefore, the primary aim of the study is to analyze the multiple impacts on health care and psychosocial well-being on these children and adolescents and their parents.
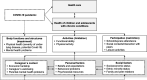
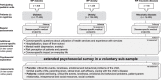
Methods: We will implement a two-stage approach. In the first step, parents and their underage children from three German patient registries for diabetes, obesity, and rheumatic diseases, are invited to fill out short questionnaires including questions about corona-specific stressors, the health care situation, and psychosocial well-being. In the next step, a more comprehensive, in-depth online survey is carried out in a smaller subsample.
Discussion: The study will provide insights into the multiple longer-term stressors during the COVID-19 pandemic in families with a child with a CC. The simultaneous consideration of medical and psycho-social endpoints will help to gain a deeper understanding of the complex interactions affecting family functioning, psychological well-being, and health care delivery.
Trial registration: German Clinical Trials Register (DRKS), no. DRKS00027974. Registered on 27th of January 2022.
Keywords: COVID-19; Children and adolescents; Chronic conditions; Diabetes; Obesity; Parents; Psychosocial strain; Rheumatic diseases; Risk perception.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Minden K, Niewerth M, Klotsche J, Zink A. Versorgung von Kindern, Jugendlichen und jungen Erwachsenen mit juveniler idiopathischer Arthritis. Akt Rheumatol. 2018;43:375–382. doi: 10.1055/a-0629-8776. - DOI
-
- Schienkiewitz A, Damerow S, Schaffrath Rosario A, Kurth B-M. Body-Mass-Index von Kindern und Jugendlichen: Prävalenzen und Verteilung unter Berücksichtigung von Untergewicht und extremer Adipositas: Ergebnisse aus KiGGS Welle 2 und Trends. [Body mass index among children and adolescents: prevalences and distribution considering underweight and extreme obesity: Results of KiGGS Wave 2 and trends] Bundesgesundheitsbl Gesundheitsforsch Gesundheitsschutz. 2019;62:1225–1234. doi: 10.1007/s00103-019-03015-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Deutsche Diabetes Gesellschaft (DDG) und diabetesDE - Deutsche Diabetes Hilfe. Deutscher Gesundheitsbericht Diabetes 2022: Die Bestandsaufnahme. Mainz: Kirchheim & Co; 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical