Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
- PMID: 36949988
- PMCID: PMC10026533
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.35131
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
Abstract
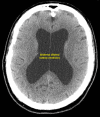
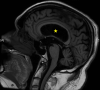
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH) occurs when there is an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid due to impeded flow or excess production, resulting in gait and memory impairment and urinary incontinence. The authors present the case of a 67-year-old male, who had symptoms for a year prior to being diagnosed. His neurological exam was significant for a slow, and unsteady wide-based gait. No underlying cause for his NPH was found. He underwent a shunt procedure following which he made a complete recovery.
Keywords: normal pressure hydrocephalus; nph; reversible dementia; ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement; vp shunt.
Copyright © 2023, Patel et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Normal pressure hydrocephalus. Finney GR. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2009;84:263–281. - PubMed
-
- A prospective study on the clinical effect of surgical treatment of normal pressure hydrocephalus: the value of hydrodynamic evaluation. Sorteberg A, Eide PK, Fremming AD. Br J Neurosurg. 2004;18:149–157. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources