Study on the mechanism of acute liver injury protection in Rhubarb anthraquinone by metabolomics based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS
- PMID: 36950014
- PMCID: PMC10025310
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1141147
Study on the mechanism of acute liver injury protection in Rhubarb anthraquinone by metabolomics based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS
Abstract
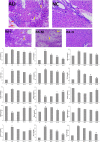
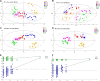
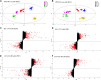
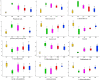
As a traditional Chinese medicine, rhubarb has been used in a variety of liver diseases and it is widely used in clinic to prevent and treat acute liver injury. Anthraquinone, as the main medicinal component of rhubarb, can reverse the further development of liver fibrosis caused by acute liver injury. In this study, metabonomics was used to explore the mechanism of different doses of rhubarb anthraquinone on acute liver injury in rats. Rhubarb anthraquinone was administered intragastric to rats at doses of 3.9, 7.8 and 15.6 mg/kg, respectively, for 7 days, and then 30% CCl4 was injected intraperitoneally at the dose of 1 ml/kg to replicate the acute liver injury model. The biochemical indicators content of ALT, AST, ALP, γ-GT, TG, TC, LDL, HDL in serum and GSH, Hyp, SOD, TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-8 in liver tissue extract were tested respectively, and liver tissue was histopathologically analysis. At the same time, UPLC-Q-TOF-MS combined with non-targeted metabolomics were used to study the metabolites and metabolic pathways of rhubarb anthraquinone in treating acute liver injury. Compared with normal rats, the contents of ALT, AST, ALP, TG, TC, LDL, γ-GT in serum and Hyp, MDA, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α in the liver tissue extract were significantly increased in model rats (p < 0.05, p < 0.01), and the content of HDL in the serum was significantly decreased (p < 0.05); the activities of GSH and SOD in liver tissue extract were also significantly decreased (p < 0.05). After administration of rhubarb anthraquinone, compared with the model group, with the increase of dosage, some biochemical indexes showed opposite changes, and gradually approached to normal rats. 12 different metabolites were identified by metabonomics, and the biosynthesis and metabolism of phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan, the metabolism of amino sugars, nucleotide sugars and pyrimidines metabolism, and the biosynthesis of steroid hormone were identified based on the biomarker analysis. Based on the biochemical analysis and metabonomics analysis of rats with acute liver injury treated with different doses of rhubarb anthraquinone, combined with histopathological observation, the results show that the protective effect of rhubarb anthraquinone on acute liver injury is related to the dosage; Meanwhile, the metabolic pathway analysis suggested that rhubarb anthraquinone alleviate acute liver injury by regulating inflammation, oxidative stress and fibrosis disorders. This study explained the therapeutic effect of rhubarb anthraquinone on acute liver injury from both material basis and action pathway, and provided safe and effective research ideas for clinical application of rhubarb.
Keywords: Rhubarb anthraquinone; UPLC-Q-ToF-MS; acute liver injury; metabolomics; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2023 Gong, Zhang, Li and Peng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Integration of pharmacodynamics and metabolomics to reveal rhubarb anthraquinone protection against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease rat model.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 3;76(4):381-390. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgae014. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38349666
-
Hepatoprotective effect and metabonomics studies of radix gentianae in rats with acute liver injury.Pharm Biol. 2021 Dec;59(1):1172-1180. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2021.1969414. Pharm Biol. 2021. PMID: 34465274 Free PMC article.
-
An integrated metabolomics strategy to reveal dose-effect relationship and therapeutic mechanisms of different efficacy of rhubarb in constipation rats.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2020 Jan 5;177:112837. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2019.112837. Epub 2019 Aug 26. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2020. PMID: 31493746
-
Study on Hepatotoxicity of Rhubarb Based on Metabolomics and Network Pharmacology.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 May 4;15:1883-1902. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S301417. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 33976539 Free PMC article.
-
[Metabolic mechanism of Prunella vulgaris in treatment of ethanol-induced oxidative stress in rats based on metabonomics].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Apr;46(7):1813-1821. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210122.503. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33982486 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Research Progress on the Anti-Liver Cancer Mechanism and Toxicity of Rhubarb Anthraquinone.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Dec 18;18:6089-6113. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S489377. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39717199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aqueous Extract of Rhubarb Promotes Hepatotoxicity via Facilitating PKM2-Mediated Aerobic Glycolysis in a Rat Model of Diethylnitrosamine-Induced Liver Cancer.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Oct 9;18:4497-4510. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S476273. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39403095 Free PMC article.
-
Protective role of ginsenoside Rg1 in the dynamic progression of liver injury to fibrosis: a preclinical meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 28;16:1512184. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1512184. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39936090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing the application of halophytic flora biomass in the management of healthcare of local people in the Salt Range of Punjab.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 4;15(1):19685. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-00961-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40467629 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen Y., Que R., Lin L., Shen Y., Liu J., Li Y. (2020). Inhibition of oxidative stress and NLRP3 inflammasome by Saikosaponin-d alleviates acute liver injury in carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatitis in mice. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 34, 2058738420950593. 10.1177/2058738420950593 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

