Polygoni Multiflori Radix interferes with bile acid metabolism homeostasis by inhibiting Fxr transcription, leading to cholestasis
- PMID: 36950015
- PMCID: PMC10025474
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1099935
Polygoni Multiflori Radix interferes with bile acid metabolism homeostasis by inhibiting Fxr transcription, leading to cholestasis
Abstract
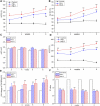
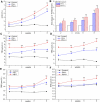
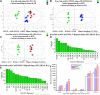
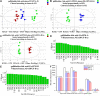
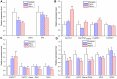
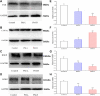
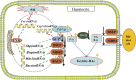
Objective: To explore the possible mechanisms of cholestasis induced by Polygoni Multiflori Radix (PM). Methods: Low and high doses of water extract of PM were given to mice by gavage for 8 weeks. The serum biochemical indexes of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), glutamyltransferase (GGT) alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and so on were detected in the second, fourth, sixth, and eighth weeks after administration. At the end of the eighth week of administration, the bile acid metabolic profiles of liver and bile were screened by high-performance liquid chromatography tandem triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (HPLC-QQQ-MS/MS). Liver pathological changes were observed by hematoxylin and eosin staining. Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was used to detect the mRNA transcription of the target genes and Western blotting (WB) was used to the detect target protein expression. Results: Biochemical tests results showed the values of ALP and GGT were two and three times greater than the normal values respectively, and the value of R was less than 2. Histopathology also showed that PM caused lymphocyte infiltration, a small amount of hepatocyte necrosis and nuclear fragmentation in mouse liver. The proliferation of bile duct epithelial cells was observed in the high group. These results indicated that PM may lead to cholestatic liver injury. HPLC-QQQ-MS/MS analysis with the multivariate statistical analysis revealed significant alterations of individual bile acids in liver and gallbladder as compared to those of the control group. RT-qPCR showed that the transcription of Fxr, Shp, Bsep, Bacs, Mdr2, and Ugt1a1 were downregulated and that of Cyp7a1, Mrp3, and Cyp3a11 was significantly upregulated in the treatment group. WB demonstrated that PM also markedly downregulated the protein expression of FXR, BSEP, and MDR2, and upregulated CYP7A1. Conclusion: PM inhibited the expression of FXR, which reduced the expression of MDR2 and BSEP, leading to the obstruction of bile acids outflow, and increased the expression of CYP7A1, resulting in an increase of intrahepatic bile acid synthesis, which can lead to cholestasis.
Keywords: Radix Polygoni Multiflori; bile acid metabolism; bile salt output pump; cholestasis; cholesterol-7α-hydroxylase; farnesoid X receptor.
Copyright © 2023 Dai, Jia, Fang, Zhu, Yan, Zhang, Wu, Feng, Liu, Huang, Li, Liu and Xiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Farnesoid X receptor contributes to oleanolic acid-induced cholestatic liver injury in mice.J Appl Toxicol. 2022 Aug;42(8):1323-1336. doi: 10.1002/jat.4298. Epub 2022 Feb 23. J Appl Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35128688 Free PMC article.
-
Astragalus saponins protect against extrahepatic and intrahepatic cholestatic liver fibrosis models by activation of farnesoid X receptor.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jan 10;318(Pt A):116833. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116833. Epub 2023 Jul 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37400008
-
Oleanolic acid alleviates ANIT-induced cholestatic liver injury by activating Fxr and Nrf2 pathways to ameliorate disordered bile acids homeostasis.Phytomedicine. 2022 Jul 20;102:154173. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154173. Epub 2022 May 14. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35605478
-
Bile salt excretory pump: biology and pathobiology.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006 Jul;43 Suppl 1:S10-6. doi: 10.1097/01.mpg.0000226385.71859.5f. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006. PMID: 16819395 Review.
-
Bile acid nuclear receptor FXR and digestive system diseases.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015 Mar;5(2):135-44. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2015.01.004. Epub 2015 Feb 25. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015. PMID: 26579439 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Emodin induced hepatic steatosis in BALb/c mice by modulating the gut microbiota composition and fatty acid metabolism.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 24;15:1516272. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1516272. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39776579 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the mechanism of emodin-induced hepatotoxicity.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 25;10(13):e33631. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33631. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39027614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol prevents gallstones in mice fed on a high fat diet via regulating PPAR-γ and SR-BI.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 17;16:1543865. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1543865. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40166468 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

