Effective treatment with mepolizumab in a patient with severe eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis complicated with small intestine perforation
- PMID: 36950026
- PMCID: PMC10025129
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2023.101818
Effective treatment with mepolizumab in a patient with severe eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis complicated with small intestine perforation
Abstract
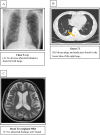
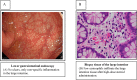
Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) is systemic vasculitis caused by eosinophilia affecting small to medium-sized blood vessels, which damages the organs. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis EGPA treatment guidelines added anti-interleukin-5 antibody mepolizumab to the standard treatment protocol for active-non-severe EGPA based on the MIRRA study. Nevertheless, the role of mepolizumab in treating patients with active severe EGPA has not been established. We treated a patient with EGPA complicated with small intestine perforation using steroid pulse intravenous, high-dose glucocorticoids, intravenous high-dose immunoglobulin therapy, and mepolizumab without immunosuppression agents; the patient went into remission, suggesting that mepolizumab is an effective therapeutic agent that could lead to remission in severe EGPA.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest associated with this manuscript.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Multi-targeted therapy for refractory eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis characterized by intracerebral hemorrhage and cardiomyopathy: a case-based review.Rheumatol Int. 2022 Nov;42(11):2069-2076. doi: 10.1007/s00296-021-04950-z. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Rheumatol Int. 2022. PMID: 34287685 Review.
-
Successful Treatment of Eosinophilic Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis: A Case of Refractory Peripheral Neuropathy and Comorbid Chronic Progressive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Treated With Mepolizumab.Cureus. 2024 Jan 12;16(1):e52192. doi: 10.7759/cureus.52192. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38222984 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis: Latest Findings and Updated Treatment Recommendations.J Clin Med. 2023 Sep 15;12(18):5996. doi: 10.3390/jcm12185996. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37762936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mepolizumab as a glucocorticoid-sparing agent in eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA): is a lower dose sufficient?J Asthma. 2021 Dec;58(12):1675-1679. doi: 10.1080/02770903.2020.1827417. Epub 2020 Oct 1. J Asthma. 2021. PMID: 32962455
-
Severe eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis responding to a combination of rituximab and mepolizumab.Am J Med Sci. 2023 Jan;365(1):93-98. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2022.07.007. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Am J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 35970248 Review.
References
-
- Sada K.E., Yamamura M., Harigai M., Fujii T., Dobashi H., Takasaki Y., et al. Classification and characteristics of Japanese patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis in a nationwide, prospective, inception cohort study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014;16:R101. doi: 10.1186/ar4550. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Faverio P., Bonaiti G., Bini F., Vaghi A., Pesci A. Mepolizumab as the first targeted treatment for eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: a review of current evidence and potential place in therapy. Therapeut. Clin. Risk Manag. 2018;14:2385–2396. doi: 10.2147/tcrm.s159949. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

