Matrix stiffness induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via Piezo1-regulated calcium flux in prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 36950111
- PMCID: PMC10025097
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106275
Matrix stiffness induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via Piezo1-regulated calcium flux in prostate cancer cells
Abstract
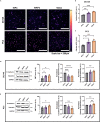
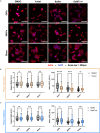
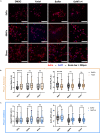
Cells utilize calcium channels as one of the main signaling mechanisms to sense changes in the extracellular space and convert these changes to intracellular signals. Calcium regulates several key signaling networks, such as the induction of EMT. The current study expands on the understanding of how EMT is controlled via the mechanosensitive calcium channel Piezo1 in cancerous cells, which senses changes in the extracellular matrix stiffness. We model the biophysical environment of healthy and cancerous prostate tissue using polyacrylamide gels of different stiffnesses. Significant increases in calcium steady-state concentration, vimentin expression, and aspect ratio, and decreases in E-cadherin expression were observed by increasing matrix stiffness and also after treatment with Yoda1, a chemical agonist of Piezo1. Overall, this study concludes that Piezo1-regulated calcium flux plays a role in prostate cancer cell metastatic potential by sensing changes in ECM stiffness and modulating EMT markers.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Cancer; Cell biology.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

