A scientometric analysis approach on the plastic sand
- PMID: 36950647
- PMCID: PMC10025159
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14457
A scientometric analysis approach on the plastic sand
Abstract
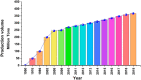
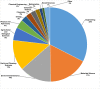
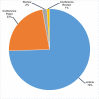
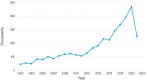
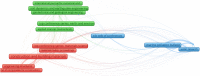
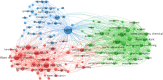
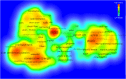
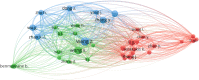
The purpose of this research was to conduct a scientometric evaluation of the literature pertaining to plastic sand in order to evaluate its many aspects. Conventional review studies have several limitations when it comes to their capacity to completely and properly link different sections of the published research. Some of the more complicated features of advanced research are co-occurrence analysis, science mapping and co-citation analysis. During the study, the most inventive authors/researchers renowned for citations, the sources with the largest number of publications, the actively involved domains, and co-occurrences of keywords in the research on plastic sand are investigated. This study is limited to scientometric analysis of the available literature data on plastic sand. The VOSviewer application (version 1.6.18) was used to perform the analysis after bibliometric data for 4512 publications were extracted from the Scopus database and utilised in the extraction process from the year 2021 to June 2022. With the support of a statistical and graphical description of researchers and nations that are contributing, this study will aid researchers in the establishment of collaborative ventures and the exchange of fresh techniques and ideas with one another.
Keywords: Plastic waste; Sand; Scientometric analysis; Sustainable material; Waste management; Waste material.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Ingabire D., Ntihemuka F., Mugabo G., Isabane R.S., Turatimana T. Recycling High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) into construction materials as a key step in plastic waste reduction: case of Kigali City, Rwanda. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. Environ. 2018;1 doi: 10.4314/rjeste.v1i1.2S. - DOI
-
- Khadke S., Gupta P., Rachakunta S., Mahata C., Dawn S., Sharma M., Verma D., Pradhan A., Krishna A.M.S., Ramakrishna S., Chakrabortty S., Saianand G., Sonar P., Biring S., Dash J.K., Dalapati G.K. Efficient plastic recycling and remolding circular economy using the technology of trust–blockchain. Sustain. Times. 2021;13:9142. doi: 10.3390/SU13169142. - DOI
-
- Lau E., Tablada A., Trivic Z., Kosori′c V.K., Todorovi′c M.T., Kaempf J.H., Goli′cgoli′c K., Peric A. Using plastic sand as a construction material toward a circular economy: a review. Sustain. Times. 2022;14:6446. doi: 10.3390/SU14116446. - DOI
-
- Babayemi J.O., Nnorom I.C., Osibanjo O., Weber R. Ensuring sustainability in plastics use in Africa: consumption, waste generation, and projections. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2019;31:1–20. doi: 10.1186/S12302-019-0254-5/FIGURES/11. - DOI
-
- Awoyera P.O., Adesina A. Plastic wastes to construction products: status, limitations and future perspective. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2020;12 doi: 10.1016/J.CSCM.2020.E00330. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

