RNA binding proteins Smaug and Cup induce CCR4-NOT-dependent deadenylation of the nanos mRNA in a reconstituted system
- PMID: 36951092
- PMCID: PMC10164591
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkad159
RNA binding proteins Smaug and Cup induce CCR4-NOT-dependent deadenylation of the nanos mRNA in a reconstituted system
Abstract
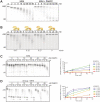
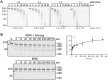
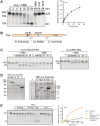
Posttranscriptional regulation of the maternal nanos mRNA is essential for the development of the anterior - posterior axis of the Drosophila embryo. The nanos RNA is regulated by the protein Smaug, which binds to Smaug recognition elements (SREs) in the nanos 3'-UTR and nucleates the assembly of a larger repressor complex including the eIF4E-T paralog Cup and five additional proteins. The Smaug-dependent complex represses translation of nanos and induces its deadenylation by the CCR4-NOT deadenylase. Here we report an in vitro reconstitution of the Drosophila CCR4-NOT complex and Smaug-dependent deadenylation. We find that Smaug by itself is sufficient to cause deadenylation by the Drosophila or human CCR4-NOT complexes in an SRE-dependent manner. CCR4-NOT subunits NOT10 and NOT11 are dispensable, but the NOT module, consisting of NOT2, NOT3 and the C-terminal part of NOT1, is required. Smaug interacts with the C-terminal domain of NOT3. Both catalytic subunits of CCR4-NOT contribute to Smaug-dependent deadenylation. Whereas the CCR4-NOT complex itself acts distributively, Smaug induces a processive behavior. The cytoplasmic poly(A) binding protein (PABPC) has a minor inhibitory effect on Smaug-dependent deadenylation. Among the additional constituents of the Smaug-dependent repressor complex, Cup also facilitates CCR4-NOT-dependent deadenylation, both independently and in cooperation with Smaug.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oskar allows nanos mRNA translation in Drosophila embryos by preventing its deadenylation by Smaug/CCR4.Development. 2006 Nov;133(22):4573-83. doi: 10.1242/dev.02649. Epub 2006 Oct 18. Development. 2006. PMID: 17050620
-
NOT10 and C2orf29/NOT11 form a conserved module of the CCR4-NOT complex that docks onto the NOT1 N-terminal domain.RNA Biol. 2013 Feb;10(2):228-44. doi: 10.4161/rna.23018. Epub 2013 Jan 9. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23303381 Free PMC article.
-
Smaug recruits the CCR4/POP2/NOT deadenylase complex to trigger maternal transcript localization in the early Drosophila embryo.Curr Biol. 2005 Feb 22;15(4):284-94. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.01.048. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 15723788
-
The Ccr4-Not Complex: Architecture and Structural Insights.Subcell Biochem. 2017;83:349-379. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46503-6_13. Subcell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28271483 Review.
-
Deadenylation of cytoplasmic mRNA by the mammalian Ccr4-Not complex.Biochem Soc Trans. 2012 Aug;40(4):896-901. doi: 10.1042/BST20120074. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012. PMID: 22817755 Review.
Cited by
-
Origin and establishment of the germline in Drosophila melanogaster.Genetics. 2025 Apr 17;229(4):iyae217. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyae217. Genetics. 2025. PMID: 40180587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Widespread regulation of the maternal transcriptome by Nanos in Drosophila.PLoS Biol. 2024 Oct 14;22(10):e3002840. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002840. eCollection 2024 Oct. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 39401257 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for binding of Drosophila Smaug to the GPCR Smoothened and to the germline inducer Oskar.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Aug 8;120(32):e2304385120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2304385120. Epub 2023 Jul 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37523566 Free PMC article.
-
Cup is essential for oskar mRNA translational repression during early Drosophila oogenesis.RNA Biol. 2023 Jan;20(1):573-587. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2023.2242650. RNA Biol. 2023. PMID: 37553798 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent innovation of protein-protein interactions in the Drosophila piRNA pathway.EMBO J. 2025 Apr 24. doi: 10.1038/s44318-025-00439-8. Online ahead of print. EMBO J. 2025. PMID: 40275032
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

