Molecular targeting of the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzymes in high-eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E refractory/relapsed acute myeloid leukemia patients: a randomized phase II trial of vismodegib, ribavirin with or without decitabine
- PMID: 36951168
- PMCID: PMC10620574
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2023.282791
Molecular targeting of the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzymes in high-eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E refractory/relapsed acute myeloid leukemia patients: a randomized phase II trial of vismodegib, ribavirin with or without decitabine
Abstract
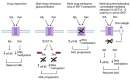
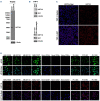
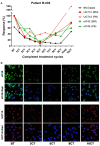
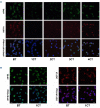
Drug resistance underpins poor outcomes in many malignancies including refractory and relapsed acute myeloid leukemia (R/R AML). Glucuronidation is a common mechanism of drug inactivation impacting many AML therapies, e.g., cytarabine, decitabine, azacytidine and venetoclax. In AML cells, the capacity for glucuronidation arises from increased production of the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A (UGT1A) enzymes. UGT1A elevation was first observed in AML patients who relapsed after response to ribavirin, a drug used to target the eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF4E, and subsequently in patients who relapsed on cytarabine. UGT1A elevation resulted from increased expression of the sonic-hedgehog transcription factor GLI1. Vismodegib inhibited GLI1, decreased UGT1A levels, reduced glucuronidation of ribavirin and cytarabine, and re-sensitized cells to these drugs. Here, we examined if UGT1A protein levels, and thus glucuronidation activity, were targetable in humans and if this corresponded to clinical response. We conducted a phase II trial using vismodegib with ribavirin, with or without decitabine, in largely heavily pre-treated patients with high-eIF4E AML. Pre-therapy molecular assessment of patients' blasts indicated highly elevated UGT1A levels relative to healthy volunteers. Among patients with partial response, blast response or prolonged stable disease, vismodegib reduced UGT1A levels, which corresponded to effective targeting of eIF4E by ribavirin. In all, our studies are the first to demonstrate that UGT1A protein, and thus glucuronidation, are targetable in humans. These studies pave the way for the development of therapies that impair glucuronidation, one of the most common drug deactivation modalities. Clinicaltrials.gov: NCT02073838.
Figures
Comment in
-
A novel approach to overcome drug resistance in acute myeloid leukemia.Haematologica. 2023 Nov 1;108(11):2889-2890. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2023.283099. Haematologica. 2023. PMID: 37165841 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- de Lima M, Roboz GJ, Platzbecker U, Craddock C, Ossenkoppele G. AML and the art of remission maintenance. Blood Rev. 2021;49:100829. - PubMed
-
- DiNardo CD, Rausch CR, Benton C, et al. . Clinical experience with the BCL2-inhibitor venetoclax in combination therapy for relapsed and refractory acute myeloid leukemia and related myeloid malignancies. Am J Hematol. 2018;93(3):401-407. - PubMed
-
- DiNardo CD, Jonas BA, Pullarkat V, et al. . Azacitidine and venetoclax in previously untreated acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(7):617-629. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

