Anti-tumor effects of miR-34a by regulating immune cells in the tumor microenvironment
- PMID: 36951490
- PMCID: PMC10242310
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.5826
Anti-tumor effects of miR-34a by regulating immune cells in the tumor microenvironment
Abstract
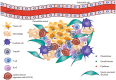
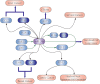
Malignant tumors pose a serious threat to human health. The development of malignant tumors is characterized by uncontrolled cell division and immune evasion. The micro-ribonucleic acid-34a (miR-34a) is a small noncoding single-stranded ribonucleic acid that is ubiquitously present in normal human tissues. However, it has been confirmed to be dysregulated in a variety of tumor cells. Numerous research have revealed the importance of miR-34a in the treatment of various malignancies. MiR-34a deletion can hasten the growth of tumors whereas miR-34a overexpression suppresses the proliferation, invasion, and migration of cancer cells. Moreover, more recent studies have highlighted its role in immunity and investigated its applicability to particular tumors. Through various immune cells, factors, and other mechanisms, miR-34a can inhibit tumor carcinogenesis. In view of the important role of miR-34a in tumors, this research reviewed the aspects of miR-34a regulation of tumor immune microenvironment to exert anti-tumor effects in order to clarify the potential immunotherapy value of miR-34a in tumors.
Keywords: antitumor; immunotherapy; miR-34a; tumor immune microenvironment.
© 2023 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non‐financial interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MiR-34a suppresses the proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer by modulating PDL1 in the immune microenvironment.Mol Cell Probes. 2020 Oct;53:101601. doi: 10.1016/j.mcp.2020.101601. Epub 2020 May 20. Mol Cell Probes. 2020. PMID: 32445780
-
MiR-34a inhibits proliferation and migration of breast cancer through down-regulation of Bcl-2 and SIRT1.Clin Exp Med. 2013 May;13(2):109-17. doi: 10.1007/s10238-012-0186-5. Epub 2012 May 24. Clin Exp Med. 2013. PMID: 22623155
-
MicroRNA-34a-5p suppresses tumorigenesis and progression of glioma and potentiates Temozolomide-induced cytotoxicity for glioma cells by targeting HMGA2.Eur J Pharmacol. 2019 Jun 5;852:42-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.03.005. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30851271
-
Tumor-derived exosomes encapsulating miR-34a promote apoptosis and inhibit migration and tumor progression of colorectal cancer cells under in vitro condition.Daru. 2021 Dec;29(2):267-278. doi: 10.1007/s40199-021-00400-0. Epub 2021 Aug 17. Daru. 2021. PMID: 34405380 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the Biotherapeutics Realm via miR-34a: "Potent Clever Little" Agent in Breast Cancer Therapy.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2019;20(8):665-673. doi: 10.2174/1389201020666190617162042. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31244419 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Different Types of Cell Death by Noncoding RNAs: Molecular Insights and Therapeutic Implications.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2025 Apr 30;8(5):1205-1226. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00681. eCollection 2025 May 9. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2025. PMID: 40370994 Review.
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer therapy: what lies beyond monoclonal antibodies?Med Oncol. 2025 Jun 19;42(7):273. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02822-1. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40536609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic value of miR-34a in Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children and its correlation with rehabilitation effect.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2024 Sep 2;19(1):507. doi: 10.1186/s13019-024-02992-5. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2024. PMID: 39223566 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Tumor Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer and Their Clinical Implications.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 May 10;47(5):347. doi: 10.3390/cimb47050347. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40699746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the role of miRNAs in cervical cancer pathogenesis and therapeutic responses.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Aug 28;12:1397945. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1397945. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39263322 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources