Identification and Characterization of a Novel Major Facilitator Superfamily Efflux Pump, SA09310, Mediating Tetracycline Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 36951566
- PMCID: PMC10112136
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.01696-22
Identification and Characterization of a Novel Major Facilitator Superfamily Efflux Pump, SA09310, Mediating Tetracycline Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
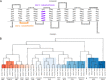
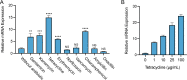
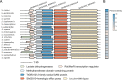
Drug efflux systems have recently been recognized as an important mechanism of multidrug resistance in bacteria. Here, we described the identification and characterization of a novel chromosomally encoded multidrug efflux pump (SA09310) in Staphylococcus aureus. SA09310 is a 43-kDa protein with 12 transmembrane helices. The conserved amino acid sequence motifs of the major facilitator superfamily (MFS) were identified in the protein SA09310, which indicated that SA09310 belonged to the MFS transporters. Expression of the sa09310 gene was induced by different types of antibiotics, including aminoglycoside, tetracycline, macrolides, and chloramphenicol. An sa09310 gene knockout mutant (Δsa09310) was constructed, and its susceptibility to 30 different antibiotics was evaluated. The Δsa09310 mutant exhibited increased sensitivity to tetracycline and doxycycline, with 64-fold- and 8-fold-decreased MICs, respectively. The mechanism of SA09310 mediation of tetracycline resistance was demonstrated by its ability to extrude intracellular tetracycline from within the cells into the environment. The efflux activity of SA09310 was further confirmed by ethidium bromide (EtBr) accumulation and efflux assays. In addition, the efflux activity of SA09310 was observed to be blocked by the known efflux pump inhibitor carbonyl cyanide chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP), which provided direct evidence that suggested the H+-dependent activity of the SA09310 efflux pump. The conservation of SA09310 homologs in Staphylococcus indicated the universal function of these SA09310-like protein clusters. In conclusion, the function-unknown protein SA09310 has been identified and characterized as a tetracycline efflux pump mediating tetracycline resistance in S. aureus.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; antibiotic resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


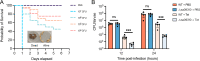
Similar articles
-
A novel member of drug/metabolite transporter (DMT) family efflux pump, SA00565, contributes to tetracycline antibiotics resistance in Staphylococcus aureus USA300.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jun 4;12(6):e0011124. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00111-24. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38651886 Free PMC article.
-
Antifungal Azoles as Tetracycline Resistance Modifiers in Staphylococcus aureus.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021 Jul 13;87(15):e0015521. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00155-21. Epub 2021 Jul 13. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33990311 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel tetracycline resistance gene, tet(63), located on a multiresistance plasmid from Staphylococcus aureus.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021 Feb 11;76(3):576-581. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkaa485. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33247717
-
Multidrug efflux pumps in Staphylococcus aureus and their clinical implications.J Microbiol. 2016 Jan;54(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007/s12275-016-5159-z. Epub 2016 Jan 5. J Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26727895 Review.
-
NorA, Tet(K), MepA, and MsrA Efflux Pumps in Staphylococcus aureus, their Inhibitors and 1,8-Naphthyridine Sulfonamides.Curr Pharm Des. 2023;29(5):323-355. doi: 10.2174/1381612829666221212101501. Curr Pharm Des. 2023. PMID: 36515045 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and characterization of a novel major facilitator superfamily (MFS) efflux pump conferring multidrug resistance in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025 May 7;69(5):e0173924. doi: 10.1128/aac.01739-24. Epub 2025 Apr 7. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025. PMID: 40192467 Free PMC article.
-
A novel member of drug/metabolite transporter (DMT) family efflux pump, SA00565, contributes to tetracycline antibiotics resistance in Staphylococcus aureus USA300.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jun 4;12(6):e0011124. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00111-24. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38651886 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence, toxin virulence genes and investigating the effect of mutations in the tetracycline gene (tetK) on the response of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to antibiotics: a study in sickle cell disease patients in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.Saudi Pharm J. 2025 Aug 25;33(5):29. doi: 10.1007/s44446-025-00033-3. Saudi Pharm J. 2025. PMID: 40853439 Free PMC article.
-
Thymoquinone' potent impairment of multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus NorA efflux pump activity.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 17;14(1):16483. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65991-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39013998 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging antibiotic resistance by various novel proteins/enzymes.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2025 Jul;44(7):1551-1566. doi: 10.1007/s10096-025-05126-4. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40232578 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

