Resilience to stress across the lifespan: Childhood maltreatment, heart rate variability, and bereavement
- PMID: 36951695
- PMCID: PMC10192121
- DOI: 10.1037/pag0000738
Resilience to stress across the lifespan: Childhood maltreatment, heart rate variability, and bereavement
Abstract
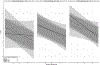
Following a stressful life event, there is considerable variation in how individuals respond and adapt. Multiple models of risk and resilience show that adverse childhood experiences may be associated with an individual's response to stress later in life. While there is considerable support that early adversity can sensitize the stress response system and lead to adverse outcomes later in life, there is mounting evidence that in adolescence and young adulthood, certain biological predispositions to stress may be associated with resilience in the context of subsequent stressors. In this study, we evaluated how individual differences in vagally mediated heart rate variability moderated the relationship between childhood maltreatment and grief among a sample of individuals experiencing a stressful life event (i.e., spousal bereavement) over time. Data were collected at approximately 3, 4.5, and 6.5 months after the death of a spouse (n = 130). Heart rate variability moderated the relationship between childhood maltreatment and grief symptoms over time (b = -0.03, p < .001), such that among individuals with more severe experiences of childhood maltreatment, those with higher heart rate variability had a faster recovery from grief than those with low heart rate variability. This research highlights an overall pattern of resilience among older adult's following spousal bereavement, as well as the relationships between childhood maltreatment, heart rate variability, and differential responses to grief following the loss of a spouse. (PsycInfo Database Record (c) 2023 APA, all rights reserved).
Figures
References
-
- Abakoumkin G, Stroebe W, & Stroebe M (2010). Does relationship quality moderate the impact of marital bereavement on depressive symptoms?. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 29(5), 510. 10.1521/jscp.2010.29.5.510 - DOI
-
- Antelmi I, De Paula RS, Shinzato AR, Peres CA, Mansur AJ, & Grupi CJ (2004). Influence of age, gender, body mass index, and functional capacity on heart rate variability in a cohort of subjects without heart disease. The American Journal of Cardiology, 93(3), 381–385. 10.1016/j.amjcard.2003.09.065 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barutcu I, Esen AM, Kaya D, Turkmen M, Karakaya O, Melek M, Esen OB, & Basaran Y (2005). Cigarette smoking and heart rate variability: Dynamic influence of parasympathetic and sympathetic maneuvers. Annals of Non-invasive Electrocardiology, 10(3), 324–329. 10.1111/j.1542-474x.2005.00636.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Basco MR, Krebaum SR, & Rush AJ (1997). Outcome measures of depression. In Strupp HH, Horowitz LM, & Lambert MJ (Eds.), Measuring patient changes in mood, anxiety, and personality disorders: Toward a core battery (p. 191–245). American Psychological Association. 10.1037/10232-007 - DOI

