A Duration-Dependent Interaction Between High-Intensity Light and Unrestricted Vision in the Drive for Myopia Control
- PMID: 36951855
- PMCID: PMC10050902
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.64.3.31
A Duration-Dependent Interaction Between High-Intensity Light and Unrestricted Vision in the Drive for Myopia Control
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the duration-dependent and synergetic impact of high-intensity light (HL) and unrestricted vision (UnV) on lens-induced myopia (LIM) development in chickens.
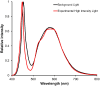
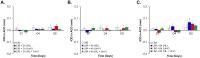
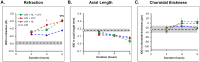
Methods: Myopia was induced in one eye in chicks (10 groups, n = 126) from day 1 posthatching (D1) until day 8 (D8) using -10 diopter (D) lenses. Fellow eyes remained uncovered as controls. Nine groups were exposed daily to 2, 4, or 6 hours of HL (15,000 lux), UnV (removal of -10 D lens), or both (HL + UnV). One group served as the LIM group without any interventions. Ocular axial length (AL), refractive error, and choroidal thickness were measured on D1, D4, and D8. Outcome measures are expressed as interocular difference (IOD = experimental eye - control eye) ± SEM.
Results: By D8, LIM increased AL (0.36 ± 0.04 mm), myopic refraction (-9.02 ± 0.37 D), and choroidal thinning (-90.27 ± 16.44 µm) in the LIM group (all, P < 0.001). Compared to the LIM group, exposure to 2, 4, or 6 hours of HL, UnV, or HL + UnV reduced myopic refraction in a duration-dependent manner, with UnV being more effective than HL (P < 0.05). Only 6 hours of HL + UnV (not 2 or 4 hours) prevented LIM and was more effective than UnV (P = 0.004) or HL (P < 0.001) in reducing myopic refraction and more effective than HL (P < 0.001) in reducing axial elongation.
Conclusions: Daily exposure to 2, 4, or 6 hours of HL, UnV, or HL + UnV reduced lens-induced myopic refraction in a duration-dependent manner in chickens. Only 6 hours of HL + UnV completely stopped LIM development. The synergetic effect of HL and UnV is dependent on the duration of the interventions.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures





References
-
- Morgan IG, French AN, Ashby RS, et al.. The epidemics of myopia: Aetiology and prevention. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2018; 62: 134–149. - PubMed
-
- Baird PN, Saw SM, Lanca C, et al.. Myopia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2020; 6(1): 1–20. - PubMed
-
- Bullimore MA, Brennan NA.. Myopia control: Why each diopter matters. Optom Vis Sci. 2019; 96(6): 463–465. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

