Prognostic value of metabolic tumor volume of extranodal involvement in diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- PMID: 36951966
- PMCID: PMC10102098
- DOI: 10.1007/s00277-023-05165-x
Prognostic value of metabolic tumor volume of extranodal involvement in diffuse large B cell lymphoma
Abstract
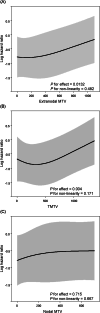
Extranodal involvement predicts poor outcomes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), but the impact of the metabolic tumor burden (MTV) of extranodal sites using positron emission tomography has not been clarified. This study aimed to assess the impact of extranodal MTV on overall survival (OS). We retrospectively analyzed 145 newly diagnosed DLBCL patients and verified the prognostic impact of each extranodal and nodal MTV. Multivariate Cox hazards modelling using both extranodal and nodal MTV as covariables identified extranodal MTV as a significant factor for OS (hazard ratio [HR] 1.072, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.019-1.129, P = 0.008), but not nodal MTV. Multivariate Cox modelling using restricted cubic splines demonstrated that the impact of total MTV depends on the MTV of extranodal sites, not of nodal sites. When both the number and MTV of extranodal involvements were used as covariables, extranodal MTV remained a significant predictor of OS (HR 1.070, 95%CI 1.017-1.127, P = 0.009), but the number of extranodal sites did not. Extranodal MTV potentially had a more significant role on prognosis than nodal MTV. When considering prognostic impacts, the MTV of extranodal involvement is significantly more important than the number.
Keywords: Diffuse large B cell lymphoma; Extranodal involvement; Metabolic tumor burden; Positron emission tomography; Prognosis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
T.Y. has received research funds and honoraria from Stargen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Mundipharma, Solasia, Pfizer, and Chugai Pharmaceutical. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical significance of metabolic tumor volume by PET/CT in stages II and III of diffuse large B cell lymphoma without extranodal site involvement.Ann Hematol. 2012 May;91(5):697-703. doi: 10.1007/s00277-011-1357-2. Epub 2011 Nov 11. Ann Hematol. 2012. PMID: 22071570 Free PMC article.
-
[Prognostic value of pretreatment (18)F-FDG PET-CT for patients with advanced diffuse large B-cell lymphoma].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2018 Jul 23;40(7):528-533. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2018.07.009. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30060362 Chinese.
-
Clinical Impact of Extranodal Metabolic Tumor Volume in 240 Diffuse Large B cell Lymphoma Patients with Extranodal Involvement.Ann Hematol. 2021 May;100(5):1221-1229. doi: 10.1007/s00277-021-04498-9. Epub 2021 Mar 25. Ann Hematol. 2021. PMID: 33768337
-
Predictive value of F-18 FDG PET/CT quantization parameters in diffuse large B cell lymphoma: a meta-analysis with 702 participants.Med Oncol. 2015 Jan;32(1):446. doi: 10.1007/s12032-014-0446-1. Epub 2014 Dec 16. Med Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25511321
-
Methodological Aspects and the Prognostic Value of Metabolic Tumor Volume assessed with 18F-FDG PET/CT in Lymphomas.Curr Radiopharm. 2022;15(4):259-270. doi: 10.2174/1874471015666220329120631. Curr Radiopharm. 2022. PMID: 35352655 Review.
Cited by
-
Baseline 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics for prognosis prediction in diffuse large B cell lymphoma with extranodal involvement.Clin Transl Oncol. 2025 Feb;27(2):727-735. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03633-y. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Clin Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39083140
-
Metabolic tumor volume from baseline [18 F]FDG PET/CT at diagnosis improves the IPI stratification in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Ann Hematol. 2024 Dec;103(12):5891-5902. doi: 10.1007/s00277-024-05717-9. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Ann Hematol. 2024. PMID: 39222121
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

