Role of sirtuins in attenuating plaque vulnerability in atherosclerosis
- PMID: 36952068
- PMCID: PMC10034899
- DOI: 10.1007/s11010-023-04714-2
Role of sirtuins in attenuating plaque vulnerability in atherosclerosis
Abstract
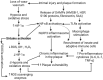
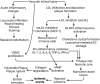
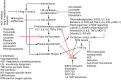
Atherosclerosis is characterized by the development of intimal plaque, thrombosis, and stenosis of the vessel lumen causing decreased blood flow and hypoxia precipitating angina. Chronic inflammation in the stable plaque renders it unstable and rupture of unstable plaques results in the formation of emboli leading to hypoxia/ischemia to the organs by occluding the terminal branches and precipitate myocardial infarction and stroke. Such delibitating events could be controlled by the strategies that prevent plaque development or plaque stabilization. Despite the use of statins to stabilize plaques, there is a need for novel targets due to continuously increasing cases of cardiovascular events. Sirtuins (SIRTs), a family of signaling proteins, are involved in sustaining genome integrity, DNA damage response and repair, modulating oxidative stress, aging, inflammation, and energy metabolism. SIRTs play a critical role in modulating inflammation and involves in the development and progression of atherosclerosis. The role of SIRTs in relation to atherosclerosis and plaque vulnerability is scarcely discussed in the literature. Since SIRTs regulate oxidative stress, inflammation, and aging, they may also regulate plaque progression and vulnerability as these molecular mechanisms underlie the pathogenesis of plaque development, progression, and vulnerability. This review critically discusses the role of SIRTs in plaque progression and vulnerability and the possibility of targeting SIRTs to attenuate plaque rupture, focusing on the highlights in genomics, molecular pathways, and cell types involved in the underlying pathophysiology.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Plaque formation; Plaque vulnerability; Sirtuins; Stable plaque; Unstable plaque.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests. All the authors have read the manuscript and declare no conflict of interest. No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of oncostatin-M in ECM remodeling and plaque vulnerability.Mol Cell Biochem. 2023 Nov;478(11):2451-2460. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04673-8. Epub 2023 Mar 1. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36856919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Different Approaches in Therapy Aiming to Stabilize an Unstable Atherosclerotic Plaque.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 21;22(9):4354. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094354. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33919446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Vascular Aging in Atherosclerotic Plaque Development and Vulnerability.Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(29):3098-3111. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666190830175424. Curr Pharm Des. 2019. PMID: 31470777 Review.
-
Inflammation and plaque vulnerability.J Intern Med. 2015 Nov;278(5):483-93. doi: 10.1111/joim.12406. Epub 2015 Aug 11. J Intern Med. 2015. PMID: 26260307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of plaque formation and rupture.Circ Res. 2014 Jun 6;114(12):1852-66. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.302721. Circ Res. 2014. PMID: 24902970 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased Oxidative Stress and Decreased Sirtuin-3 and FOXO3 Expression Following Carotid Artery Intimal Injury in Hyperlipidemic Yucatan Microswine.Cardiol Cardiovasc Med. 2024;8(1):33-42. doi: 10.26502/fccm.92920355. Epub 2024 Jan 22. Cardiol Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38333571 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidized Low-density Lipoproteins and Lipopolysaccharides Augment Carotid Artery Plaque Vulnerability in Hypercholesterolemic Microswine.Cardiol Cardiovasc Med. 2023;7(4):273-294. doi: 10.26502/fccm.92920338. Epub 2023 Jul 26. Cardiol Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37577745 Free PMC article.
-
Thromboembolism in the Complications of Long COVID-19.Cardiol Cardiovasc Med. 2023;7(2):123-128. doi: 10.26502/fccm.92920317. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Cardiol Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37389402 Free PMC article.
-
Glycolipid Metabolic Disorders, Metainflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Cardiovascular Diseases: Unraveling Pathways.Biology (Basel). 2024 Jul 12;13(7):519. doi: 10.3390/biology13070519. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39056712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirtuins as Players in the Signal Transduction of Citrus Flavonoids.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 6;25(4):1956. doi: 10.3390/ijms25041956. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396635 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Organization WH. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). Fact sheet. Reviewed June 2016. cited 2016-08-26. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs317/en
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

