Early Identification of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 4 Years - Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2020
- PMID: 36952289
- PMCID: PMC10042615
- DOI: 10.15585/mmwr.ss7201a1
Early Identification of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 4 Years - Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2020
Abstract
Problem/condition: Autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
Period covered: 2020.
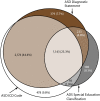
Description of system: The Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network is an active surveillance program that estimates prevalence and characteristics of ASD and monitors timing of ASD identification among children aged 4 and 8 years. In 2020, a total of 11 sites (located in Arizona, Arkansas, California, Georgia, Maryland, Minnesota, Missouri, New Jersey, Tennessee, Utah, and Wisconsin) conducted surveillance of ASD among children aged 4 and 8 years and suspected ASD among children aged 4 years. Surveillance included children who lived in the surveillance area at any time during 2020. Children were classified as having ASD if they ever received 1) an ASD diagnostic statement in an evaluation, 2) a special education classification of autism (eligibility), or 3) an ASD International Classification of Diseases (ICD) code (revisions 9 or 10). Children aged 4 years were classified as having suspected ASD if they did not meet the case definition for ASD but had a documented qualified professional's statement indicating a suspicion of ASD. This report focuses on children aged 4 years in 2020 compared with children aged 8 years in 2020.
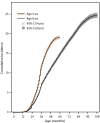
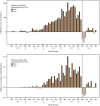
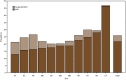
Results: For 2020, ASD prevalence among children aged 4 years varied across sites, from 12.7 per 1,000 children in Utah to 46.4 in California. The overall prevalence was 21.5 and was higher among boys than girls at every site. Compared with non-Hispanic White children, ASD prevalence was 1.8 times as high among Hispanic, 1.6 times as high among non-Hispanic Black, 1.4 times as high among Asian or Pacific Islander, and 1.2 times as high among multiracial children. Among the 58.3% of children aged 4 years with ASD and information on intellectual ability, 48.5% had an IQ score of ≤70 on their most recent IQ test or an examiner's statement of intellectual disability. Among children with a documented developmental evaluation, 78.0% were evaluated by age 36 months. Children aged 4 years had a higher cumulative incidence of ASD diagnosis or eligibility by age 48 months compared with children aged 8 years at all sites; risk ratios ranged from 1.3 in New Jersey and Utah to 2.0 in Tennessee. In the 6 months before the March 2020 COVID-19 pandemic declaration by the World Health Organization, there were 1,593 more evaluations and 1.89 more ASD identifications per 1,000 children aged 4 years than children aged 8 years received 4 years earlier. After the COVID-19 pandemic declaration, this pattern reversed: in the 6 months after pandemic onset, there were 217 fewer evaluations and 0.26 fewer identifications per 1,000 children aged 4 years than children aged 8 years received 4 years earlier. Patterns of evaluation and identification varied among sites, but there was not recovery to pre-COVID-19 pandemic levels by the end of 2020 at most sites or overall. For 2020, prevalence of suspected ASD ranged from 0.5 (California) to 10.4 (Arkansas) per 1,000 children aged 4 years, with an increase from 2018 at five sites (Arizona, Arkansas, Maryland, New Jersey, and Utah). Demographic and cognitive characteristics of children aged 4 years with suspected ASD were similar to children aged 4 years with ASD.
Interpretation: A wide range of prevalence of ASD by age 4 years was observed, suggesting differences in early ASD identification practices among communities. At all sites, cumulative incidence of ASD by age 48 months among children aged 4 years was higher compared with children aged 8 years in 2020, indicating improvements in early identification of ASD. Higher numbers of evaluations and rates of identification were evident among children aged 4 years until the COVID-19 pandemic onset in 2020. Sustained lower levels of ASD evaluations and identification seen at a majority of sites after the pandemic onset could indicate disruptions in typical practices in evaluations and identification for health service providers and schools through the end of 2020. Sites with more recovery could indicate successful strategies to mitigate service interruption, such as pivoting to telehealth approaches for evaluation.
Public health action: From 2016 through February of 2020, ASD evaluation and identification among the cohort of children aged 4 years was outpacing ASD evaluation and identification 4 years earlier (from 2012 until March 2016) among the cohort of children aged 8 years in 2020 . From 2016 to March 2020, ASD evaluation and identification among the cohort of children aged 4 years was outpacing that among children aged 8 years in 2020 from 2012 until March 2016. The disruptions in evaluation that coincided with the start of the COVID-19 pandemic and the increase in prevalence of suspected ASD in 2020 could have led to delays in ASD identification and interventions. Communities could evaluate the impact of these disruptions as children in affected cohorts age and consider strategies to mitigate service disruptions caused by future public health emergencies.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed and submitted the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors form for disclosure of potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services, Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. Healthy People 2030 ASD goals. Washington DC: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2022. https://health.gov/healthypeople/custom-list?ids=31387+31386
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
