Effectiveness and safety of immune checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy in advanced upper tract urothelial carcinoma: A multicenter, retrospective, real-world study
- PMID: 36952461
- PMCID: PMC10225242
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.5796
Effectiveness and safety of immune checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy in advanced upper tract urothelial carcinoma: A multicenter, retrospective, real-world study
Abstract
Introduction: The effectiveness and safety of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) monotherapy in advanced upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) is less reported.
Methods: In total, 106 consecutive advanced UTUC patients receiving ICI monotherapy were collected from nine high volume centers. Clinical outcomes were analyzed according to multiple parameters (e.g., treatment line, metastatic sites). Objective response rate (ORR), overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were captured after ICI initiation.
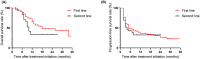
Results: With a median follow-up of 12.0 months, 25 patients in the first-line group and 15 patients in the second-line group died of UTUC. We reported a median OS of 18.0 months, a median PFS of 5.0 months, and an ORR of 38.6% for patients in the first-line group; a median OS of 10.0 months, a median OS of 4.0 months, and an ORR of 27.8% for patients in the second-line group. Complete response was observed in two patients in the first-line group and one patient in the second-line group with a total complete response rate of 2.8%. In the univariate and multivariate analysis, visceral metastasis with a hazard ratio of 2.4 was associate with poor OS. The most common treatment-related adverse events included fatigue (11.3%), pruritus (10.4%), and diarrhea (6.6%).
Conclusions: This real-world study suggests that ICI monotherapy is active and has acceptable toxic effects for unresectable or metastatic UTUC as first-line therapy in cisplatin-ineligible patients or second-line therapy in platinum-refractory patients.
Keywords: advanced UTUC; cisplatin-ineligible; immune checkpoint inhibitor.
© 2023 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

