Niraparib and Abiraterone Acetate for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 36952634
- PMCID: PMC10431499
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.22.01649
Niraparib and Abiraterone Acetate for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) remains a lethal disease with current standard-of-care therapies. Homologous recombination repair (HRR) gene alterations, including BRCA1/2 alterations, can sensitize cancer cells to poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibition, which may improve outcomes in treatment-naïve mCRPC when combined with androgen receptor signaling inhibition.
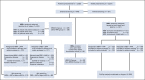
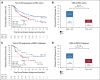
Methods: MAGNITUDE (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03748641) is a phase III, randomized, double-blinded study that evaluates niraparib and abiraterone acetate plus prednisone (niraparib + AAP) in patients with (HRR+, n = 423) or without (HRR-, n = 247) HRR-associated gene alterations, as prospectively determined by tissue/plasma-based assays. Patients were assigned 1:1 to receive niraparib + AAP or placebo + AAP. The primary end point, radiographic progression-free survival (rPFS) assessed by central review, was evaluated first in the BRCA1/2 subgroup and then in the full HRR+ cohort, with secondary end points analyzed for the full HRR+ cohort if rPFS was statistically significant. A futility analysis was preplanned in the HRR- cohort.
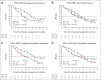
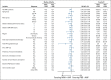
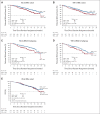
Results: Median rPFS in the BRCA1/2 subgroup was significantly longer in the niraparib + AAP group compared with the placebo + AAP group (16.6 v 10.9 months; hazard ratio [HR], 0.53; 95% CI, 0.36 to 0.79; P = .001). In the overall HRR+ cohort, rPFS was significantly longer in the niraparib + AAP group compared with the placebo + AAP group (16.5 v 13.7 months; HR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.56 to 0.96; P = .022). These findings were supported by improvement in the secondary end points of time to symptomatic progression and time to initiation of cytotoxic chemotherapy. In the HRR- cohort, futility was declared per the prespecified criteria. Treatment with niraparib + AAP was tolerable, with anemia and hypertension as the most reported grade ≥ 3 adverse events.
Conclusion: Combination treatment with niraparib + AAP significantly lengthened rPFS in patients with HRR+ mCRPC compared with standard-of-care AAP.
[Media: see text].
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Figures
Comment in
-
Combining Poly(ADP)-Ribose Polymerase Inhibitors With Abiraterone in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Is Biomarker Testing Necessary?J Clin Oncol. 2023 Jun 20;41(18):3291-3294. doi: 10.1200/JCO.23.00270. Epub 2023 Mar 23. J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36952642 No abstract available.
-
Re: Niraparib and Abiraterone Acetate for Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer.Eur Urol. 2023 Oct;84(4):437-438. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2023.04.029. Epub 2023 May 11. Eur Urol. 2023. PMID: 37179239 No abstract available.
-
Re: Niraparib and Abiraterone Acetate for Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer.Eur Urol. 2024 Jan;85(1):96-97. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2023.09.012. Epub 2023 Sep 27. Eur Urol. 2024. PMID: 37775360 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ryan CJ, Smith MR, Fizazi K, et al. : Abiraterone acetate plus prednisone versus placebo plus prednisone in chemotherapy-naive men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (COU-AA-302): Final overall survival analysis of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 16:152-160, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Khalaf DJ, Annala M, Taavitsainen S, et al. : Optimal sequencing of enzalutamide and abiraterone acetate plus prednisone in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 2, crossover trial. Lancet Oncol 20:1730-1739, 2019 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

