The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic upon pancreatic cancer treatment (CONTACT Study): a UK national observational cohort study
- PMID: 36959376
- PMCID: PMC10035482
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-023-02220-2
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic upon pancreatic cancer treatment (CONTACT Study): a UK national observational cohort study
Abstract
Introduction: CONTACT is a national multidisciplinary study assessing the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic upon diagnostic and treatment pathways among patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).
Methods: The treatment of consecutive patients with newly diagnosed PDAC from a pre-COVID-19 pandemic cohort (07/01/2019-03/03/2019) were compared to a cohort diagnosed during the first wave of the UK pandemic ('COVID' cohort, 16/03/2020-10/05/2020), with 12-month follow-up.
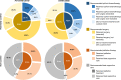
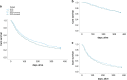
Results: Among 984 patients (pre-COVID: n = 483, COVID: n = 501), the COVID cohort was less likely to receive staging investigations other than CT scanning (29.5% vs. 37.2%, p = 0.010). Among patients treated with curative intent, there was a reduction in the proportion of patients recommended surgery (54.5% vs. 76.6%, p = 0.001) and increase in the proportion recommended upfront chemotherapy (45.5% vs. 23.4%, p = 0.002). Among patients on a non-curative pathway, fewer patients were recommended (47.4% vs. 57.3%, p = 0.004) or received palliative anti-cancer therapy (20.5% vs. 26.5%, p = 0.045). Ultimately, fewer patients in the COVID cohort underwent surgical resection (6.4% vs. 9.3%, p = 0.036), whilst more patients received no anti-cancer treatment (69.3% vs. 59.2% p = 0.009). Despite these differences, there was no difference in median overall survival between the COVID and pre-COVID cohorts, (3.5 (IQR 2.8-4.1) vs. 4.4 (IQR 3.6-5.2) months, p = 0.093).
Conclusion: Pathways for patients with PDAC were significantly disrupted during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic, with fewer patients receiving standard treatments. However, no significant impact on survival was discerned.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Collaborative C. Elective surgery cancellations due to the COVID-19 pandemic: global predictive modelling to inform surgical recovery plans. 2020; Available from: www.bjs.co.uk. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Onder G, Rezza G, Brusaferro S. Case-fatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID-19 in Italy. J Am Med Assoc. 2020;323:1775–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

