Role of intrarenal resistive index and ElastPQ® renal shear modulus in early diagnosis and follow-up of diabetic nephropathy: A prospective study
- PMID: 36959891
- PMCID: PMC10028382
- DOI: 10.1177/1742271X20942249
Role of intrarenal resistive index and ElastPQ® renal shear modulus in early diagnosis and follow-up of diabetic nephropathy: A prospective study
Abstract
Introduction: We aimed to establish baseline normal values of ElastPQ® (Philips Healthcare, Bothell, Washington, USA) renal shear modulus, evaluate changes in intrarenal resistive index and renal shear modulus in various stages of diabetic nephropathy, their diagnostic potential and role in follow-up.
Methods: Our prospective observational study was performed over two years. In total, 130 adult cases with diabetic nephropathy and 130 normal adult controls were selected. Diabetic nephropathy was confirmed by persistent albuminuria on 24-hour urinary albumin testing at three month intervals and staged by albuminuria quantification. Measurement of intrarenal resistive index and renal shear modulus in all subjects was performed and their variation with stage of nephropathy was statistically analyzed using Pearson's correlation. Receiver operating characteristic curves were plotted and their individual and combined diagnostic potentials were assessed. Statistical significance was tested using t tests and analysis of variance. Interrater agreement was tested using Cohen's kappa coefficient.
Results: Mean intrarenal resistive index was significantly higher for cases (mean 0.72 ± 0.05) than controls (mean 0.62 ± 0.04) and showed significant age variation (p < 0.05). Normal values of ElastPQ® renal shear modulus ranged from 3.87 to 4.72 kPa and was significantly higher for cases (mean 8.59 ± 1.77 kPa) than controls (mean 4.32 ± 0.45 kPa) and showed significant differences between each stage of nephropathy, being highest in stage 2. Maximum diagnostic accuracy was at 0.65 (sensitivity 90%, specificity 76.2%, area under curve 0.916) for intrarenal resistive index and at 5.31 kPa (sensitivity 90.8%, specificity 84.6%, area under curve 0.923) for renal shear modulus. Combination of the two further improved diagnostic performance (highest accuracy of 89%, sensitivity 81.7%, specificity 96.3%).
Conclusions: Normal range of ElastPQ® renal shear modulus values could be established. Intrarenal resistive index and renal shear modulus can be used as imaging parameters for early diagnosis and follow-up of diabetic nephropathy.
Keywords: Diabetic nephropathy; ElastPQ®; renal Doppler; renal elastography; renal shear modulus.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
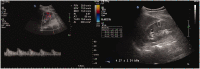


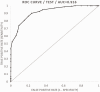

Similar articles
-
Resistive Index of Intrarenal Artery in Evaluation of Diabetic Nephropathy.Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull. 2015 Dec;41(3):125-130. doi: 10.3329/bmrcb.v41i3.29888. Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull. 2015. PMID: 29870167
-
Placental elastography in second trimester preeclampsia prediction: A prospective study.Ultrasound. 2022 Aug;30(3):228-235. doi: 10.1177/1742271X211040543. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Ultrasound. 2022. PMID: 35936967 Free PMC article.
-
Magnitude dependent discordance in liver stiffness measurements using elastography point quantification with transient elastography as the reference test.Eur Radiol. 2019 May;29(5):2448-2456. doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5831-2. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Eur Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30488108
-
Value of Doppler ultrasound in early detection of diabetic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Ultrasound. 2021 Aug;29(3):141-149. doi: 10.1177/1742271X20977051. Epub 2020 Dec 8. Ultrasound. 2021. PMID: 34567226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The stages in diabetic renal disease. With emphasis on the stage of incipient diabetic nephropathy.Diabetes. 1983 May;32 Suppl 2:64-78. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.2.s64. Diabetes. 1983. PMID: 6400670 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of shearing wave elastography in detecting early diabetic nephropathy.Ir J Med Sci. 2025 Apr;194(2):529-535. doi: 10.1007/s11845-025-03897-5. Epub 2025 Feb 6. Ir J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39912978 Free PMC article.
-
Current Insights into the Significance of the Renal Resistive Index in Kidney and Cardiovascular Disease.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 May 10;13(10):1687. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13101687. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37238172 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
