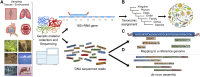
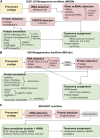
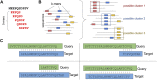
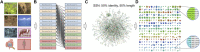
Exploring microbial functional biodiversity at the protein family level-From metagenomic sequence reads to annotated protein clusters
- PMID: 36959975
- PMCID: PMC10029925
- DOI: 10.3389/fbinf.2023.1157956
Exploring microbial functional biodiversity at the protein family level-From metagenomic sequence reads to annotated protein clusters
Abstract
Metagenomics has enabled accessing the genetic repertoire of natural microbial communities. Metagenome shotgun sequencing has become the method of choice for studying and classifying microorganisms from various environments. To this end, several methods have been developed to process and analyze the sequence data from raw reads to end-products such as predicted protein sequences or families. In this article, we provide a thorough review to simplify such processes and discuss the alternative methodologies that can be followed in order to explore biodiversity at the protein family level. We provide details for analysis tools and we comment on their scalability as well as their advantages and disadvantages. Finally, we report the available data repositories and recommend various approaches for protein family annotation related to phylogenetic distribution, structure prediction and metadata enrichment.
Keywords: biodiversity; cluster annotation; metagenomes; metatranscriptomes; microbial dark matter; protein clustering; protein families.
Copyright © 2023 Baltoumas, Karatzas, Paez-Espino, Venetsianou, Aplakidou, Oulas, Finn, Ovchinnikov, Pafilis, Kyrpides and Pavlopoulos.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures